新闻中心



2018年7月2日晚,随着第八届上海“数字未来”工作营DigitalFUTURES YOUNG系列活动第三场学员研讨会的成功开展,DigitalFUTURES YOUNG系列活动在工作营期间已暂告一段落。活动期间主办方组织了三场研讨会,总共超过200人次参与,其中17名优秀学员上台分享了各自的研究成果,就数字设计与智能建造领域的一系列问题与各位导师与学员进行了深入的探讨。
As the last Workshop Student Seminar in the DigitalFUTURES YOUNG program was organized successfully on the night of July 2nd 2018, the DigitalFUTURES YOUNG program has come to an end during the workshop. There are three seminars in the program, in which more than 200 supervisors and students in total participated. 17 outstanding students gave lectures on their research and had a discussion with the audience in the field of computational design and digital fabrication.


从计算机辅助到计算机决策
From Computer-Aided to Computer-Decided
郑豪
Hao Zheng
郑豪现为宾夕法尼亚大学设计学院的博士生。他是程序员以及设计研究员,研究领域为机器学习、机器人技术、混合现实以及生成设计。郑豪认为,许多数字建造和AR辅助设计等虽然极其依赖计算机的辅助,但最终都是人工来进行和完成的。他最初开发的计算机决策设计模型仍然是主流的图像-图像的模式,而这个模型的问题就是受限于像素点。之后他对于模型进行了优化,他尝试从一种新的角度来理解建筑平面,使得新模型在输入的时候是以矢量而不是图像的方式,由此计算机计算和学习的速度得到了飞跃式的增长。郑豪认为,人工智能+机器人建造合作完成建筑从生成设计到实际建造的全套流程将成为未来的趋势。所以当我们面对未来的冲击时,建筑师应如何面对并找到自己的位置是一个关键点问题。
Hao Zheng is currently a Ph.D student at the University of Pennsylvania, School of Design. He is a programmer and design researcher, specializing in machine learning, robotic technology, mixed reality, and generative design. Hao Zheng believes that although plenty of digital construction and AR-aided design seem to rely heavily on computer assistance, the work are actually completed manually. The computer decision-making model he originally developed is still the mainstream image-image model, and the problem with this model is the limitation of the pixel points. After that, he optimized the model. He tried to understand the building plan from a new perspective, so that the new model was input as a vector rather than an image, and the speed of computer calculation and learning increased a lot. Hao Zheng believes that it is artificial intelligence-robot cooperation to construct buildings from design to fabrication that will become the future trend. When we face the shock of digital future, it is a key issue for architects to find their orientation.

人机工程学参数化设计
Ergonomics Parametric Design
曾绍庭
Shaoting Zeng
曾绍庭是清华大学美术学院工业设计系设计学博士,研究方向是设计形态学数字形态设计。曾绍庭从对参数化的理解切入,他认为参数化最重要的两点为关系+参数,其中他对参数获取的想法与人机工程学紧密相关。他认为如何将人机工程学与参数化结合的关键在于生成一词。随后他向我们介绍了他的两个个项目,生成座椅及眼镜。学员们对于曾绍庭在完成这两个实际项目中运用的插件和算法表现出来了强烈的兴趣,同时也对座椅和眼镜的设计提出了多种建议并与曾绍庭共同探讨,例如椅子如何做到定制化,是否可以做到动态调整、眼镜的参数从何而来、是否可用传感器和3D扫描获取人体数据等。大家在激烈的讨论中碰撞出了思想的火花。
Shaoting Zeng is Ph.D of Design, Department of Industrial Design, Academy of Art and Design, Tsinghua University. His research direction is about morphology digital form design. Shaoting Zeng cuts in the topic from the understanding of parametric. He believes that the two most important points of parametric are relationship and parameters, and his idea of parameter acquisition is closely related to ergonomics. He believes that the key to combining ergonomics with parametric is to generate the word. He then introduced us to his two projects, generating seats and glasses. The participants showed great interest in Zeng Shaoting's plug-ins and algorithms used in completing these two practical projects. He also put forward various suggestions for the design of the seats and glasses and discussed with Shaoting Zeng , such as how to customize the chair. Whether it can be dynamically adjusted, where the parameters of the glasses come from, whether sensors and 3D scans can be used to obtain human body data. Spark of thought has been born from the heated discussion.
遗传算法在找形和多目标性能优化的应用
Applications of Genetic Algorithms in Form Finding and Multi-Objective Optimization
钱秦阳
Qinyang Qian
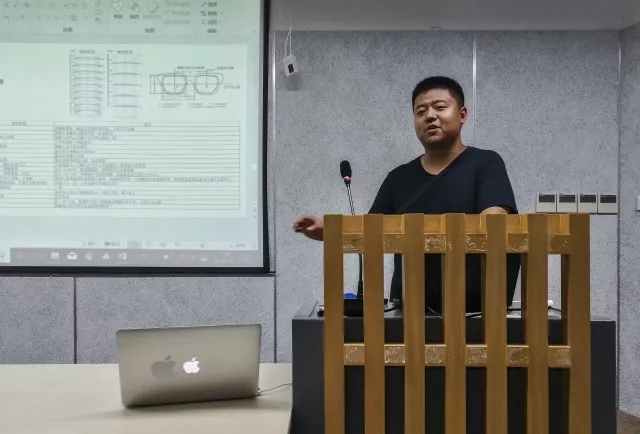
钱秦阳是一个喜欢从数据合理性开始设计的设计师,他来自伦敦大学学院(建筑环境),擅长可持续建筑设计、遗传算法、风、光、热环境及舒适度分析以及BIM技术的协同运用。钱秦阳以一个自己的方案来讲解遗传算法的运用。方案以热舒适分析作为出发点,将其量化为多个指标,建立基因库(几何形)),而表型就(外窗)随之发生变化。基因库-参数化建模-性能分析-遗传算法优化这整个流程,针对不同侧重得到了两千多种解决方案。他选择了热舒适度较为均衡的方案作为最终选择。随后,钱秦阳对这个方案进行了总结,提出了可以优化的方向。仿生vs有机?“人类在面对挑战时,从自然中抽象出良好的设计理念,是一种通过模仿自然界经过时间考验的模式和策略来寻求可持续发展的解决方案”
Qinyang Qian, a designer who likes to start the design from data rationality, UCL Bartlett, Architecture (Building Environment), good at sustainable architecture design, genetic algorithms, wind, daylight, thermal and comfort analysis in built environment, BIM application and collaboration. Qinyang Qian uses his own project to explain the application of genetic algorithms. The program uses thermal comfort analysis as a starting point, quantifies it into multiple indicators, builds a gene pool (geometry), and the phenotype (outer window) changes accordingly. Genebank-Parametric Modeling-Performance Analysis-Genetic Algorithm Optimization This process has more than 2,000 solutions for different focuses. He chose a more balanced approach to thermal comfort as the final choice. Subsequently, Qian Qinyang summarized this plan and proposed a direction that can be optimized. Bionic vs organic? “Humans abstract a good design concept from nature in the face of challenges. It is a solution to seek sustainable development by imitating the time-tested patterns and strategies of nature”.
基于大气污染控制的城市街区与建筑高度及布局的优化策略研究
The Optimization of the Height and the Arrangement of Buildings in An Urban Block with An Approach of Controlling Air Pollution
Zeynab Kaseb
Zeynab是伊朗Shahid Beheshti大学建筑技术专业的硕士生,她的研究领域专注于计算流体动力学(CFD)和城市通风。众所周知,实地的全面测量受限于昂贵的仪器、不可控的环境因素以及复杂的校准程序。所以Zeynab的目标是让风的舒适度控制在行人适应的程度、减少空气污染以及改善的城市通风。她使用了Butterfly插件及遗传算法,前者允许用户与分析结果来交互,并加载CFD模拟的结果;后者通过模拟自然进化过程搜索最优解的方法来辅助生成解决方案。她以一个街区为例得出的三种布置方法,说明了建筑高度在城市设计以及大气污染控制中的重要性。
Zeynab is a master student of architectural technology, Shahid Beheshti University in Iran, while her research area is focusing on CFD and urban ventilation. As we know, comprehensive measurements are limited by expensive instruments, uncontrollable environmental factors, and complex calibration procedures. Zeynab’s goal is to comfort the wind to the pedestrian level, reduce air pollution and improve urban ventilation. She uses butterfly for grasshopper to allow users to interact with the analysis results and load the results of the CFD simulation. She also uses genetic algorithm to generate a solution by simulating the natural evolution process to search for the optimal solution. She utilizes three methods of one block as an example to illustrate the importance of building height in urban design and the control of air pollution.

DigitalFUTURES YOUNG 青年学者研讨会由姚佳伟博士主持,上台学员均对自己在数字设计与智能建造领域的研究和实践作了精彩的演讲。研讨会受到了学员的极大欢迎,会议现场座无虚席,与会学员踊跃发言,热烈讨论,效果远超主办方预期。至此,DigitalFUTURES YOUNG 青年学者研讨会已圆满收官,欢迎大家继续关注DigitalFUTURES 2018的其他后续活动。
DigitalFUTURES YOUNG Workshop Students Seminar was hosted by Prof. Jiawei Yao, in which students gave excellent speeches about their research and practice. The seminars enjoy a good reputation and students flocked to it. All the participants had a lively discussion, which is far more than the DigitalFUTURES YOUNG Workshop Students Seminar Organizer’s expectation. And until now, DigitalFUTURES YOUNG Workshop Students Seminar has ended up and welcome everyone to focus on other activities in DigitalFUTURES 2018.



DigitalFUTURES YOUNG│青年学者计划
本届工作营推出了DigitalFUTURES YOUNG青年学者计划,包括为期三晚的工作营学员研讨会,旨在为全球数字化设计与建造领域的青年学者们提供学术交流分享的平台,展示DigitalFUTURES Shanghai 2018的优秀学员及学术成果。
The workshop launches DigitalFUTURES YOUNG including workshop student seminars, which aims to provide a platform for young scholars in the field of computational design and digital fabrication and to introduce outstanding students as well as their impressive achievement.


