新闻中心



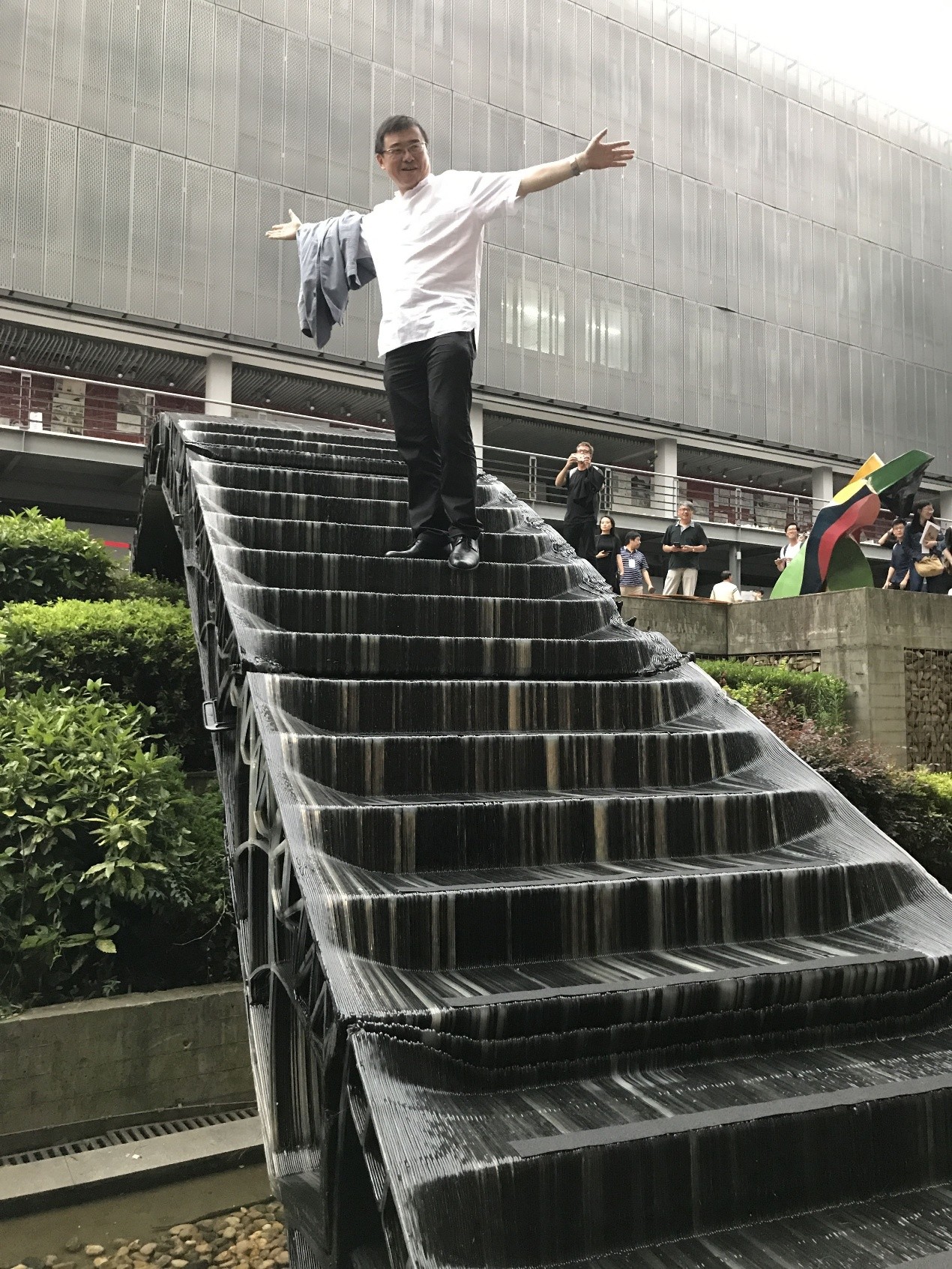
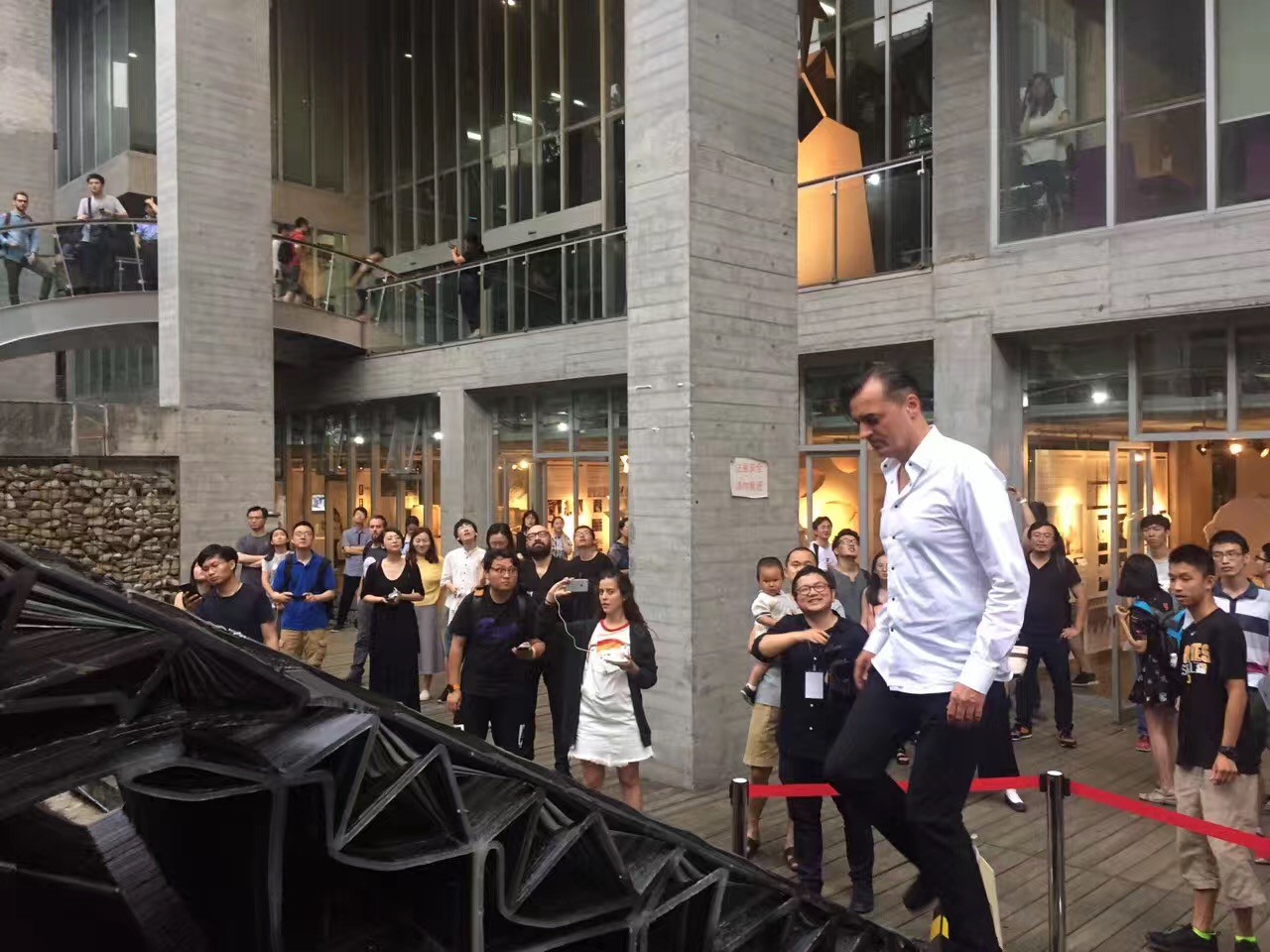
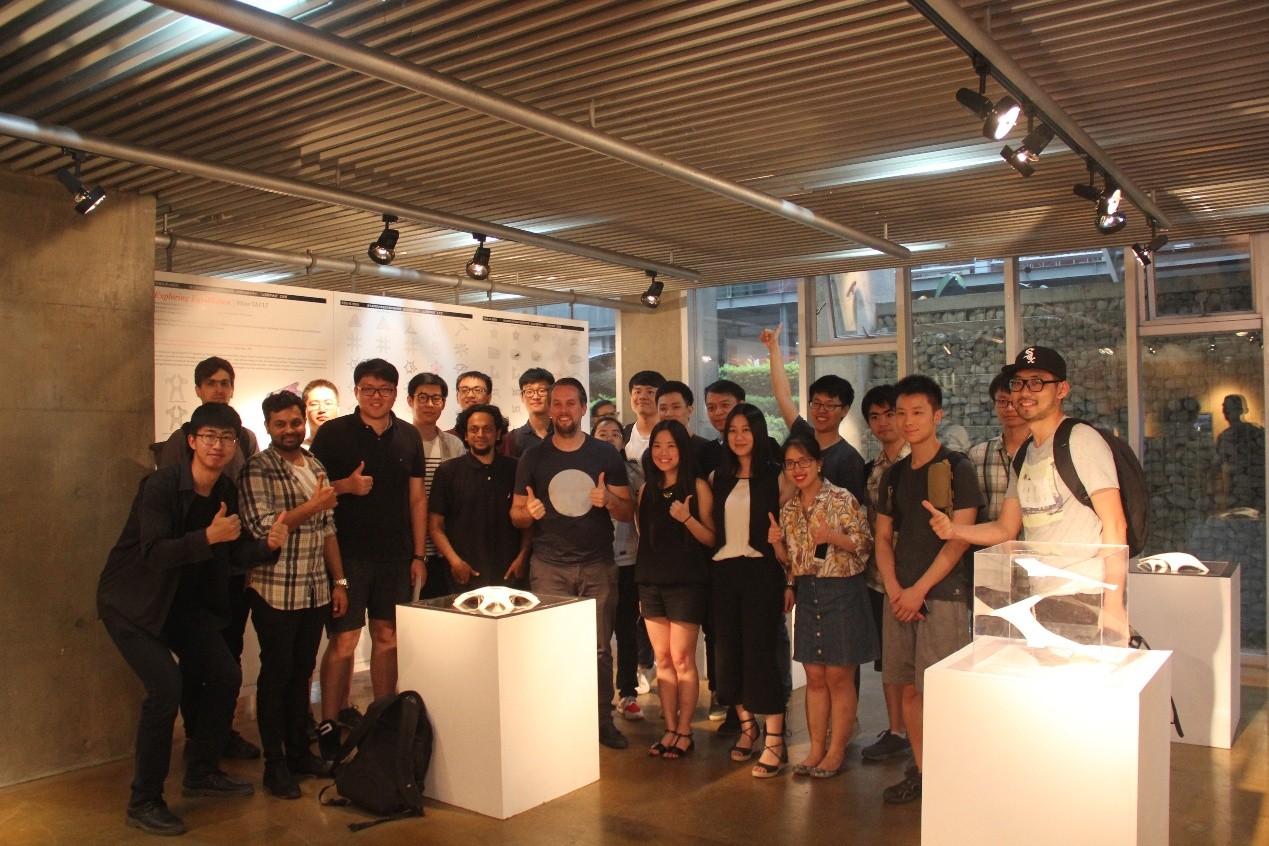
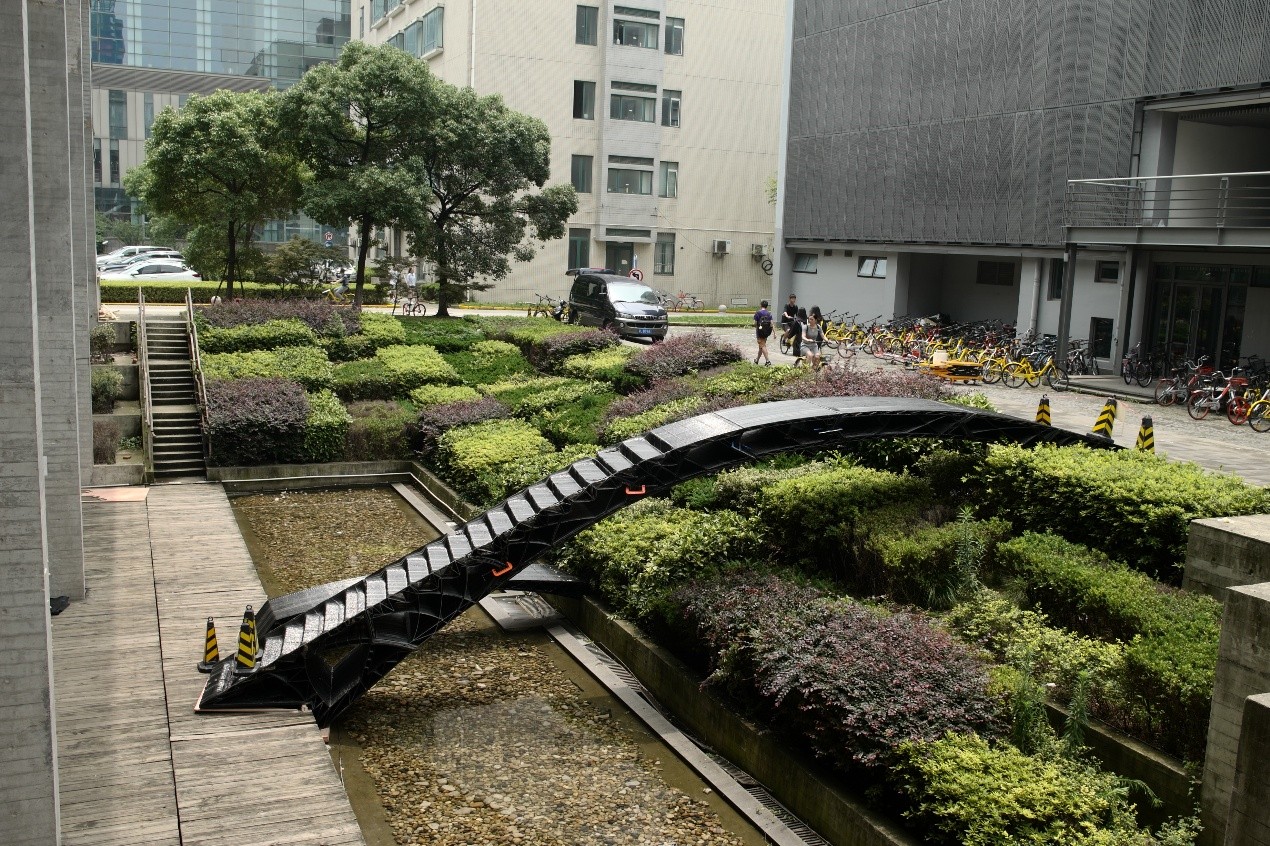
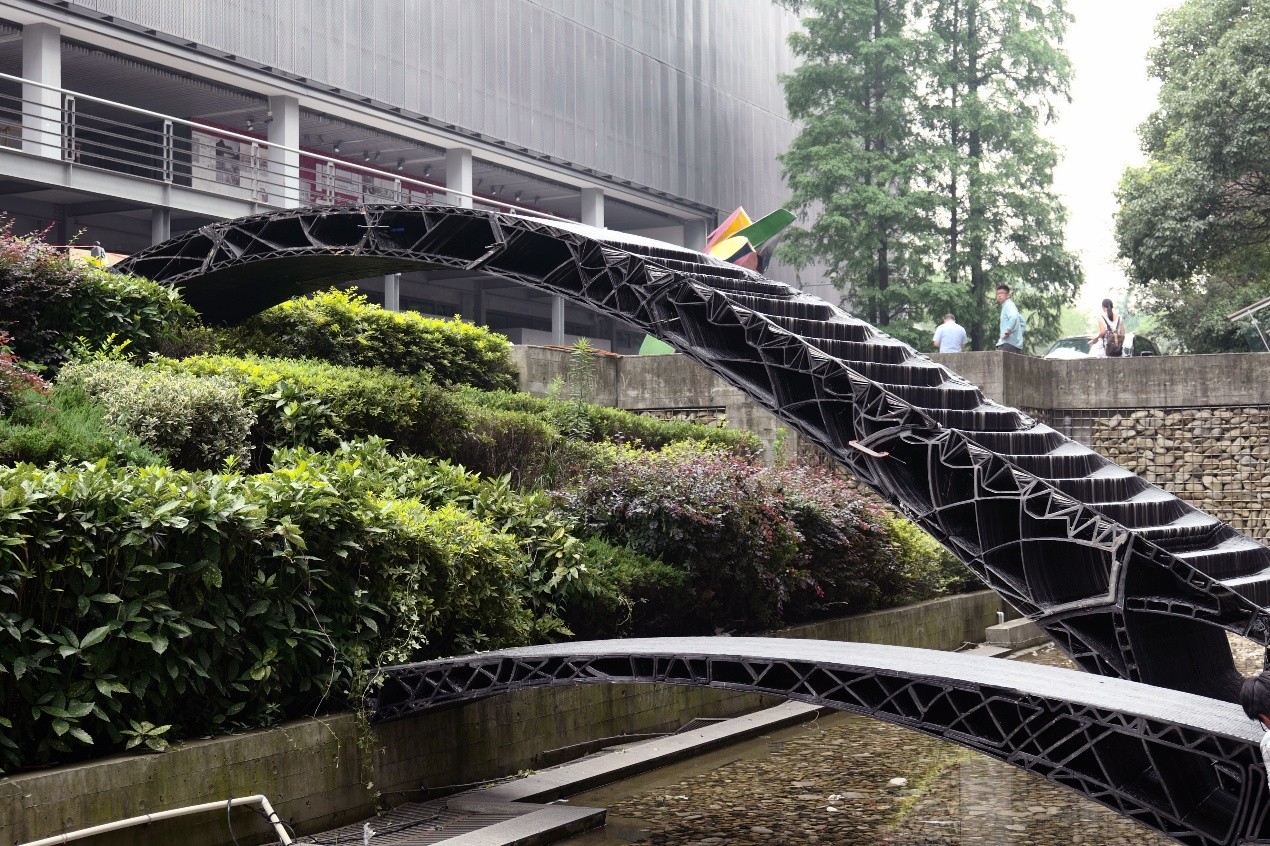
2017年6月24日至7月2日,第七届“上海数字未来”系列活动在同济大学建筑与城市规划学院成功举办。于同济大学建筑与城市规划学院门口架设了一组使用3D打印技术制造的桥,跨度分别达到4m和11m

2017“数字未来”系列活动以“可视化VS物质化”为主题,通过数字建造全新诠释材料的物质主义,旨在通过对材料本体特性与数字化生产的有效整合,探求通过“建造与自动化”等方面体现“数字化物质设计”的新途径。本次活动旨在召集全世界最先锋的数字设计和建造领域的组织与个体,在上海建筑数字建筑工程技术研究中心、同济大学建筑与城市规划学院和同济大学建筑设计研究院(集团)有限公司的推动下,以及中国数字建筑设计专业委员会(DADA)、全国高等学校建筑学科专业指导委员会-建筑数字技术教学工作委员会、一造科技Fab-Union的支持下,探讨以唯物论为依据的材料数字时代的哲学思维为新兴数控建造产业带来的新挑战和新机遇。

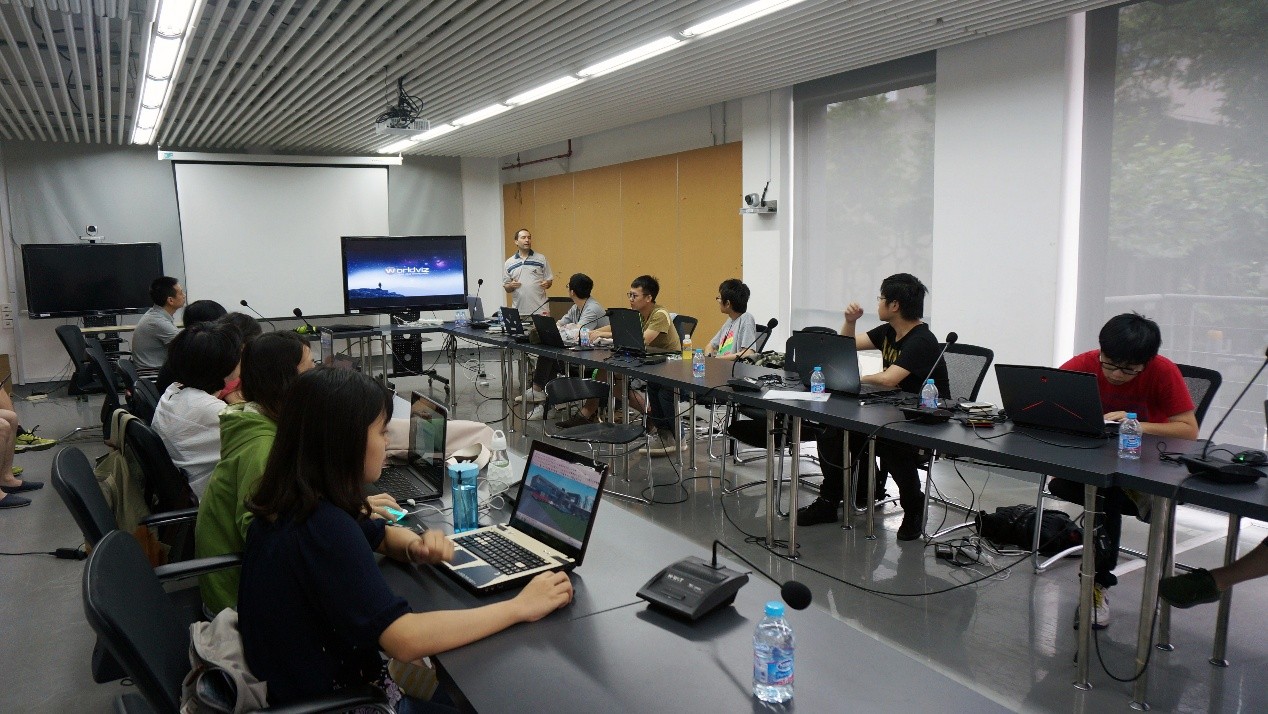
7月2日8:00-18:30,第七届“上海数字未来”国际会议在同济大学建筑设计研究院(集团)有限公司一楼大报告厅举行。此次国际学术会议邀请到了来自国内外的10位演讲嘉宾,为我们呈现了关于“可视化VS物质化”这一主题的不同探索。首先由同济大学建筑设计研究院(集团)有限公司总裁丁洁民对会议开幕发表了致辞,接着在同济大学建筑与城市规划学院袁烽教授的主持下,10位嘉宾发表了各自的演讲。



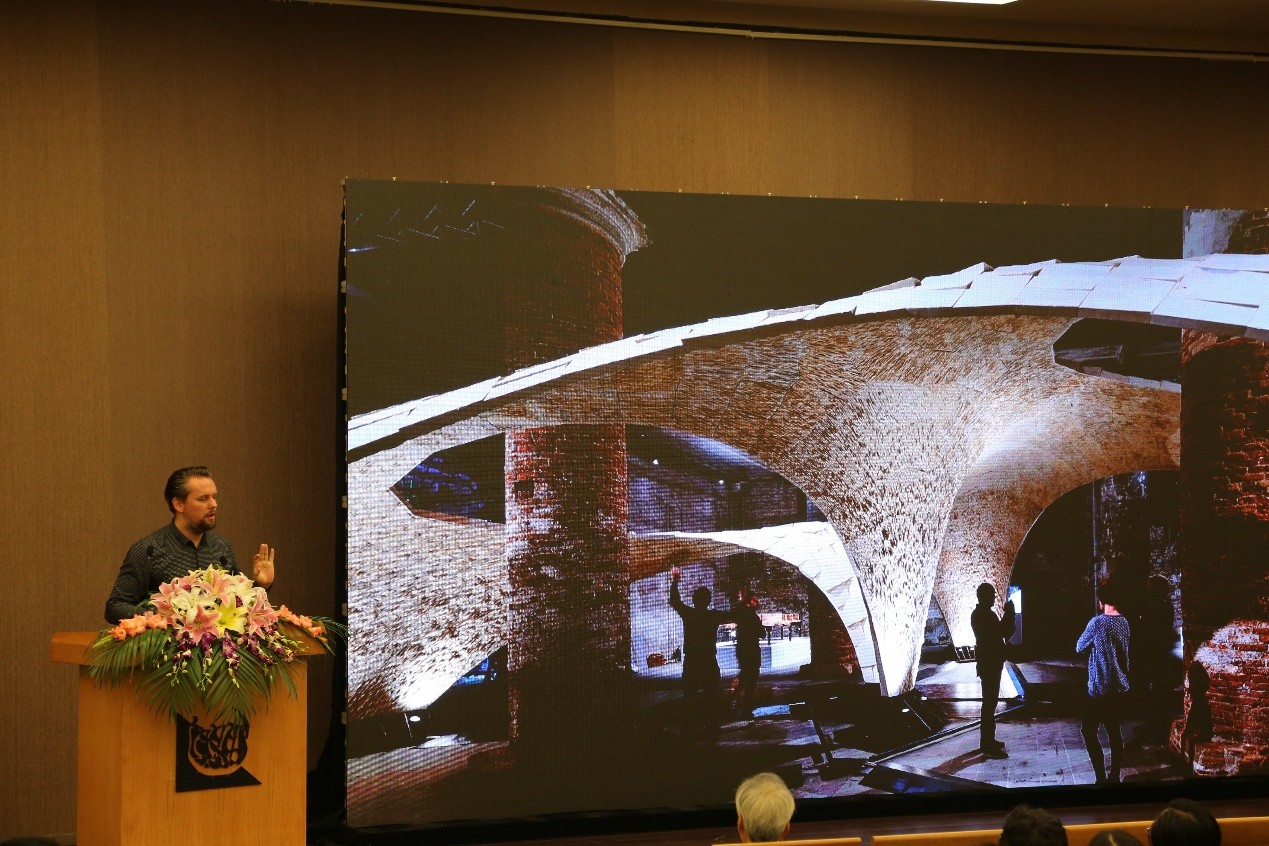
第一位演讲嘉宾是来自瑞士苏黎世联邦理工学院(ETH)的Philippe Block,他的演讲主题是”Beyond Bending: Learning from the Master Building”。Philippe Block教授在世界各地讲课,并与诸如Foster + Partners,Zaha Hadid Architects,Herzog&de Meuron,SOM结构和Studio Olafur Eliasson等设计机构合作,他的作品已在2009年美国纽约市设计三年展、2012年和2016年威尼斯建筑双年展上展出。Philippe Block教授在ETH与他的博士Tom Van Mele一起指导Block Research Group(BRG),BRG专注于平衡分析,计算形式生成,曲面结构的优化与曲面制造。作为Ochsendorf,DeJong&Block,LLC的合伙人,他将他的研究应用于历史古迹和设计的结构评估和新型压缩结构的工程,他的研究赢得了无数奖项。
在讲座中Philippe Block教授首先介绍了历史砖石结构的平衡分析,接着介绍了对实现平衡的新的图解方法的探索,以实现轻质的拱形及有效的表面结构,从而达到超越砖石的设计。纵观历史,大师们在经济,效率和优雅的限制下发现表现形式,我们应该从建筑和结构原理,设计和分析方法以及施工逻辑中学到很多东西,在建筑遗产基础上开发新颖的结构设计方法,Philippe Block教授以一系列建筑实践案例展现了自己的探索,有:MLK Jr. Park Vault、MIT Collier纪念馆、Armadillo Vault等。

来自东京城市大学的渡边诚教授以“Can AI Make Designs ? AIrchitect ← Architectural Intelligence”为主题发表演讲,渡边诚是渡边诚建筑事务所主持建筑师,曾执教于岡山県立大学和台湾淡江大学。他的作品的特点是运动感和触觉感知,使来访者想要触摸它;而在理论上,通过对设计行为的言语化和持续探索翻译成计算机程序来传达出来。他是2013/2014年算法设计探索国际程序竞赛、2015年算法设计探索国际座谈会的组织者,他的作品曾荣获多项奖项,包括2002年的日本建筑学会大奖,1997年美国景观设计师协会大奖等。
渡边诚认为,建筑应该在虚拟的世界中自然生长,数码技术将为人类带来新的建筑文化。一方面,建筑设计软件有强大的数据处理能力,而对于东京这样的高密度城市,需要关注的问题非常复杂,借助软件实现的建筑设计可以实现对这些因素的分析及模拟。另一方面,数码技术不能成为主宰力量,它需要建筑师用自己的经验和直觉进行修正,而AI技术正是实现这一目标的黑箱,应该实现以人工智能(AI)的电脑逻辑运算来辅助建筑设计,在数字程序里体现情感和温度。

长江学者特聘教授孙澄以“基于虚拟智能的建筑物质性能探索(Exploring the Materialization Performance of Architecture Based on Virtual Intelligence )”为主题发表演讲。孙澄教授现任哈尔滨工业大学建筑学院党委书记兼副院长,国家级建筑虚拟仿真实验教学中心主任,中国建筑学会常务理事,全国高校建筑学学科专业指导委员会数工委副主任,曾获中国建筑学会青年建筑师奖、黑龙江省杰出青年基金,其长期致力于数字化建筑设计、公共建筑创作等方面的研究。
孙澄教授首先回顾了物质性能导向的设计思维的演化过程,从主观决策思维,到生成设计思维,最后到性能驱动思维,他认为主观决策思维未充分发挥虚拟智能对可能性的探索,而生成设计思维则未能发挥设计者对设计决策过程的控制,而性能驱动思维则避免了这些缺陷。接下来孙澄教授提出建筑设计的虚拟智能技术革新,并从建筑与环境信息动态集成技术、设计参数与物质性能映射技术、多性能导向设计决策支持技术、CANN-BIM建筑数字化设计平台几个方面介绍了虚拟智能技术革新,最后以一个实际项目介绍了自己在实践中对实现建筑物质性能的探索。

来自Zaha Hadid建筑事务所的 Shajay Bhooshan以“Parametric design thinking-Practise-embedded Architectural Research: a Decade of CODE”为主题发表演讲。 Shajay Bhooshan于2007年加入扎哈·哈迪德建筑事务所,一直专注于建筑概念和生产,将理论话语应用到生产制造。作为事务所计算设计研究组(CODE)的联合创始人,Shajay还拥有编程、数学以及工业机器人的专业知识,更是在壳体结构的建筑应用和节点方面作出了巨大贡献。
Shajay Bhooshan首先从建筑三要素:坚固、适用、美观开始,重新思索参数设计。介绍ZHCODE从基于物理的设计和基于社会的设计,基于物理的设计包括因素有结构限制、建造限制,基于社会的设计则是基于用户的代理模型进行研究。关于基于物理的设计,Shajay从计算机辅助几何设计、共有的几何语言、累积的及协作的设计进行了介绍,并通过一系列例子说明建筑几何、数字建造和空间数据的关系。
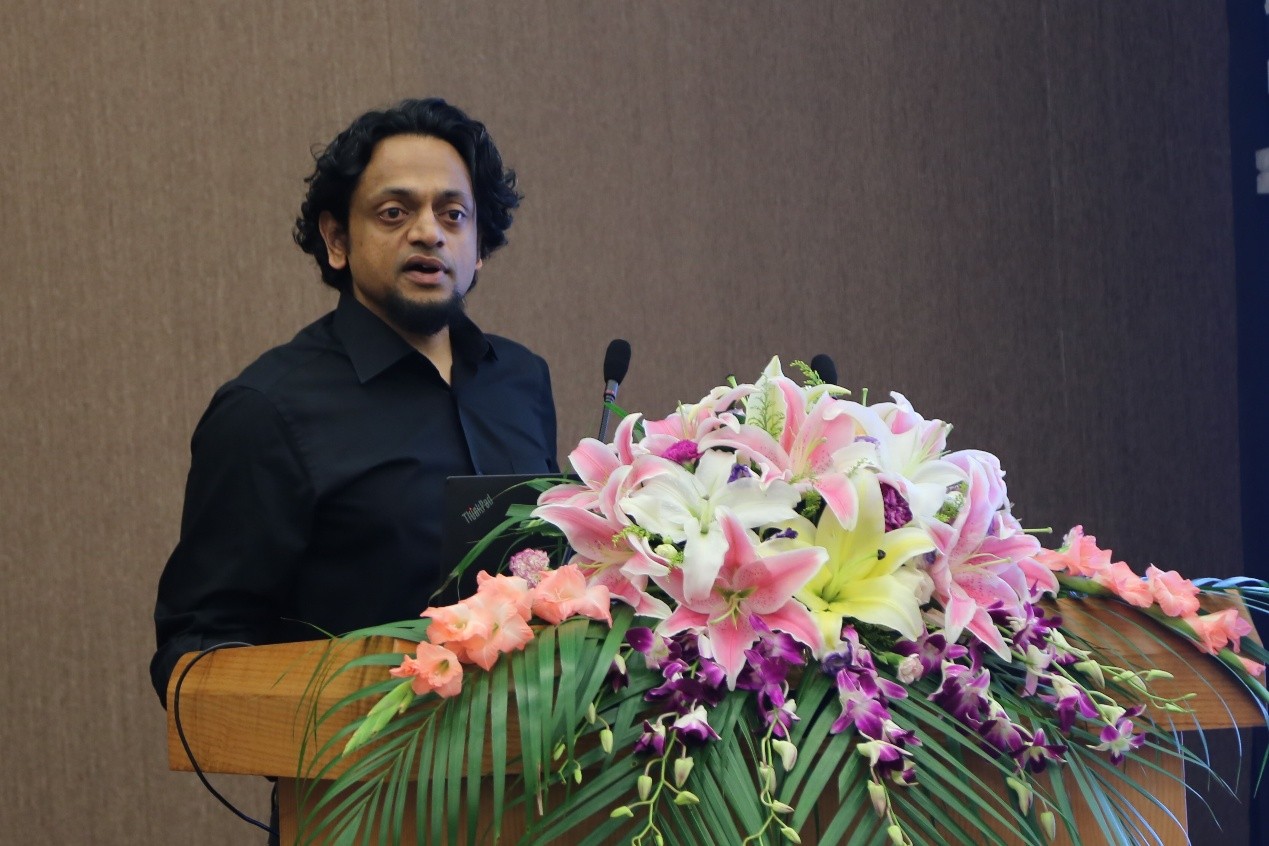

来自美国南加州大学建筑系的教授以“Size Matters: The Limits of Representation”为主题发表演讲。建筑师兼理论家,策展人。同济大学建筑与城规学院客座教授,美国哈佛大学设计研究生院客座教授,欧洲科学院院士,曾执教于多所国际顶尖大学,其理论研究论文众多,自1998年至2017年在国际出版众多书目。
认为建筑师应该同时关注“形式的呈现”和形式的内在属性,因为在不同的尺度下,虽然形式的外在呈现可能是一样的,但是内在属性由于尺寸的变化而完全不同的了。

经过中午短暂的午休,下午的会议由同济建筑设计研究院(集团)有限公司技术发展部副主任张峥主持。
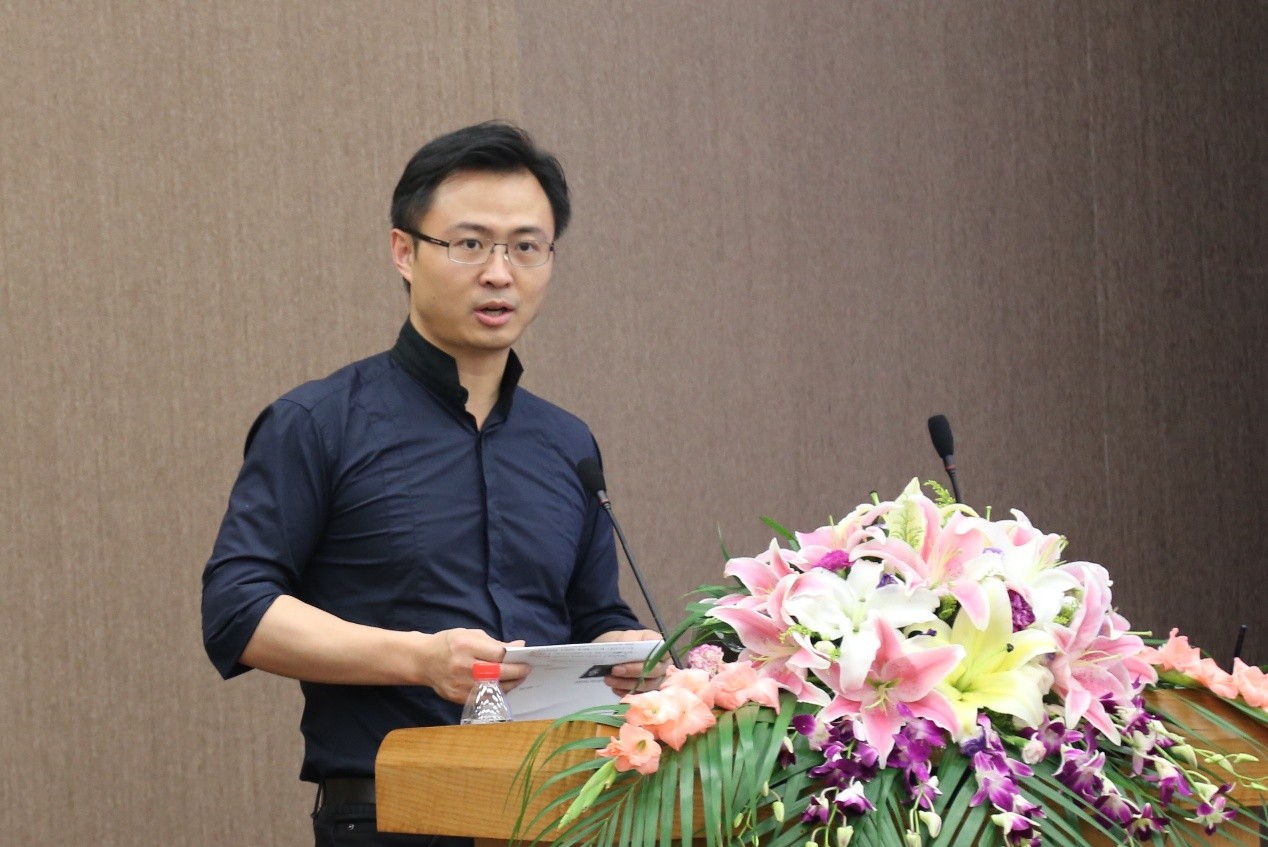

亚洲计算机辅助建筑设计学会(CAADRIA)主席Hyunsoo Lee以“Biomimetic Inspired Facade Design for Aesthetically Well-Designed Architectural Space”为主题发表演讲。Hyunsoo Lee是亚洲计算机辅助建筑设计学会(CAADRIA)主席,韩国延世大学教授,首尔建筑设计与规划顾问委员会顾问,其研究领域包括生物建筑,老年人住房和数字化建造。他的研究兴趣还在建筑立面和材料技术相结合的数字制作。
Hyunsoo Lee演讲包括仿生灵感设计的两类主题:一个是灵感来自鸟群的智慧,并解释了如何根据居民的行为来控制建筑立面的百叶窗,描述了通过解释鸟群植树行为,通过立面进行百叶窗控制;第二个主题是开发使用模仿自然形式创作的韩国传统绘画的门面图案设计过程。该演讲总结了使用仿生设计方法的想法,该方法可以是建立精心设计的空间的最强大的方法之一。

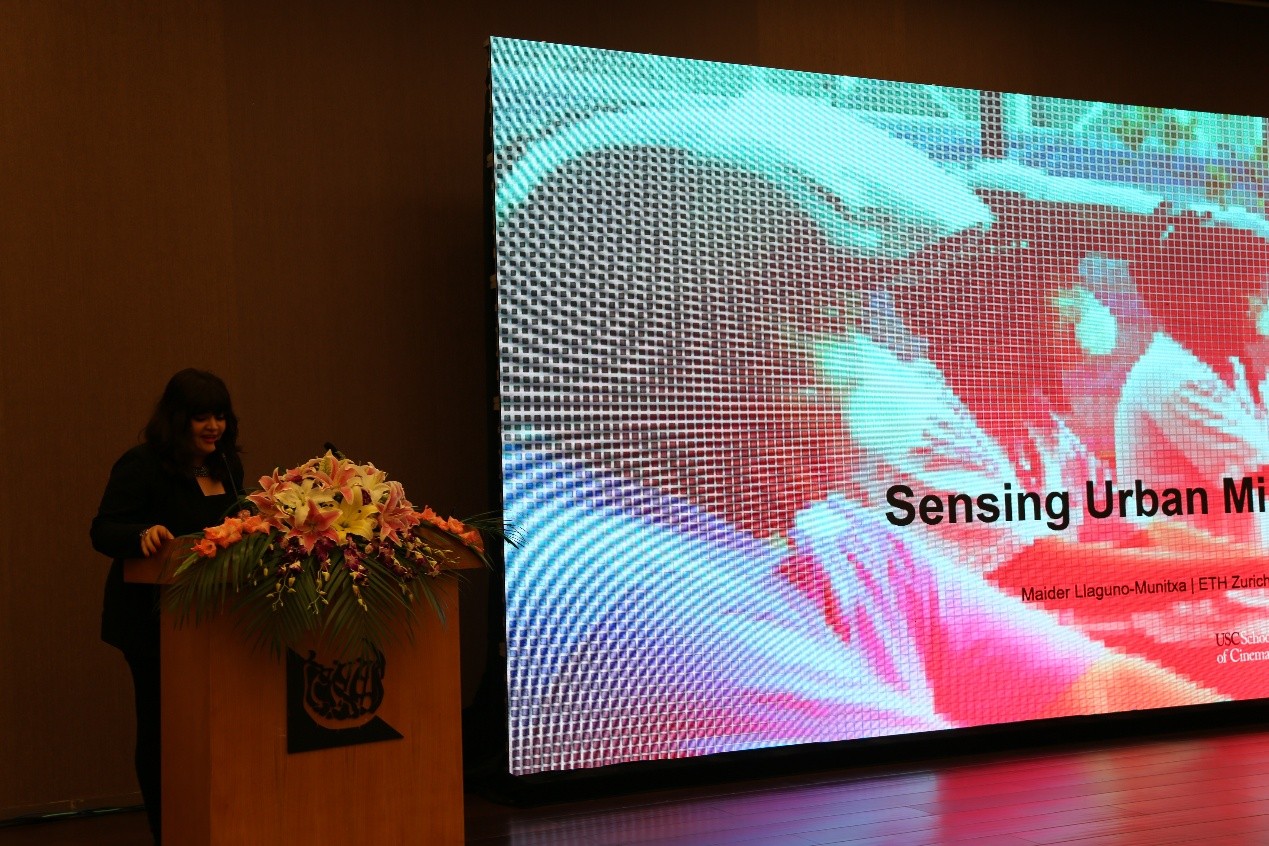
建筑师和互动媒体设计师Biayna Bogosian以“Sensing Urban Microclimates”为主题发表演讲。Biayna Bogosian研究感知和认知交互设计,特别是城市与环境数据模式之间的关系,是洛杉矶“Somewhere Something”工作室的负责人,在建筑,城市设计,互动设计和数字制作的交互领域工作,改变大众的认知和建设城市的方式。自2011年以来,Biayna在哥伦比亚大学建筑规划与保护研究生院和南加大建筑学院教授数字媒体和建筑设计课程。
Biayna介绍了感知城市微观气候的相关技术,通过分离各种气候变量并将其分配给可视化装置的不同附件,手机高精度的气候数据,如:二氧化碳&一氧化碳浓度、温度、空气湿度,可视化的方式增加了大众对建筑环境感知的敏感度,同时决定了在模拟的三维空间中的装置行为。

来自清华大学建筑学院的黄蔚欣副教授以“有机结构与数据空间(Organic Structure & Data Space)”为主题发表演讲。 黄蔚欣于日本京都大学博士毕业,现任清华大学建筑学院副教授,全国高校建筑学学科专业指导委员会数工委副主任,亚洲计算机辅助建筑设计学会(CAADRIA)组织官员,数字建筑设计专业委员会(DADA)委员,DADA2013数字建筑国际会议总协调人,近10年来一直在从事数字技术与建筑设计相结合的跨学科研究和教学工作。
黄蔚欣指出“性能化设计”是建筑设计的一种本质性诉求,建筑需求的很多方面都可以被量化为性能,并能够整合在一个包含“生成”与“检验”的数字化设计流程中,使用数据进行分析。区别于传统建筑设计常采用的几何原型,当代数字建筑设计更关注自然有机形态(organic form),自然有机形态是由组成系统的众多个体在运动中相互作用,逐步演化而成,而这个动态过程与“信息生成形态”的概念是一致的。黄蔚欣教授试图探讨建筑性能(特别是结构性能)信息经过数字化转译而得到自然有机形态的途径,并通过多个案例展现了对这一主题的探索。
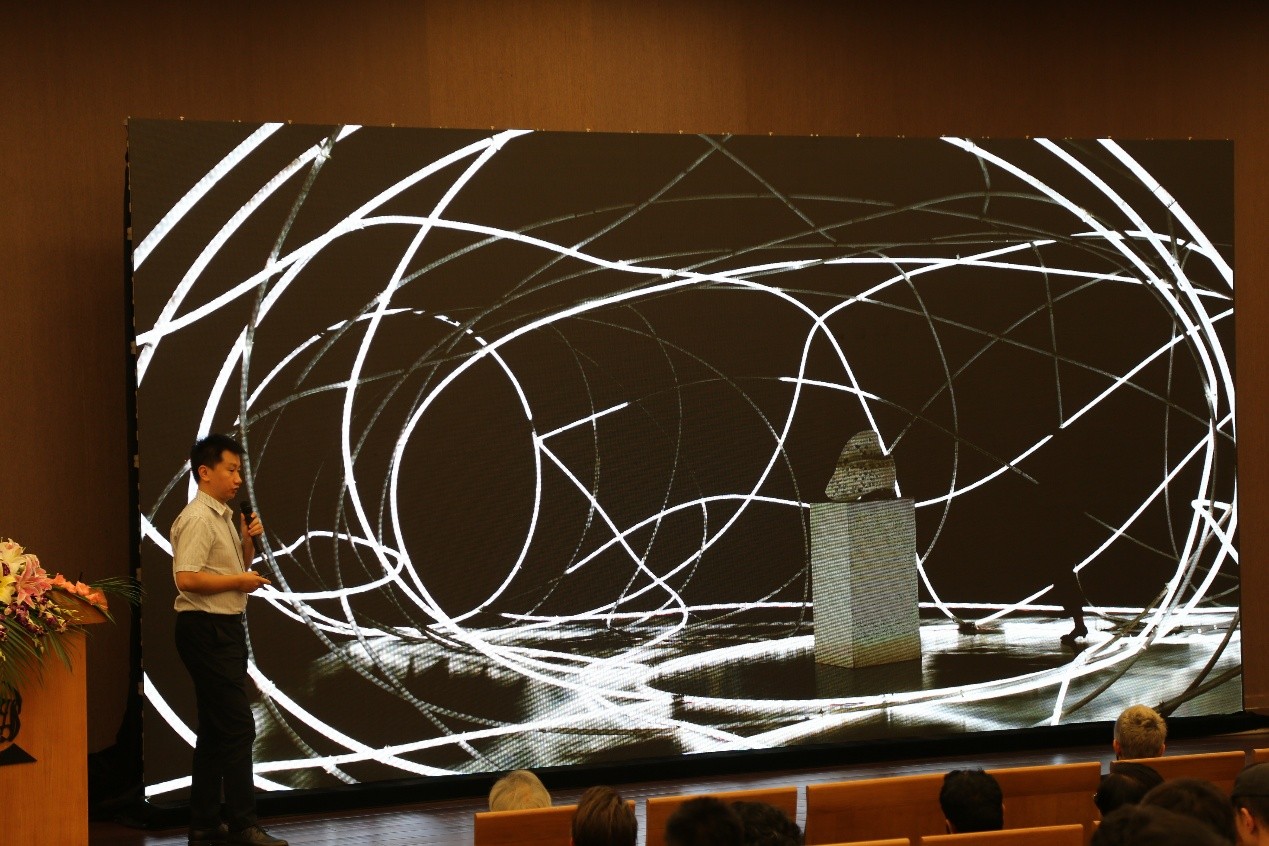

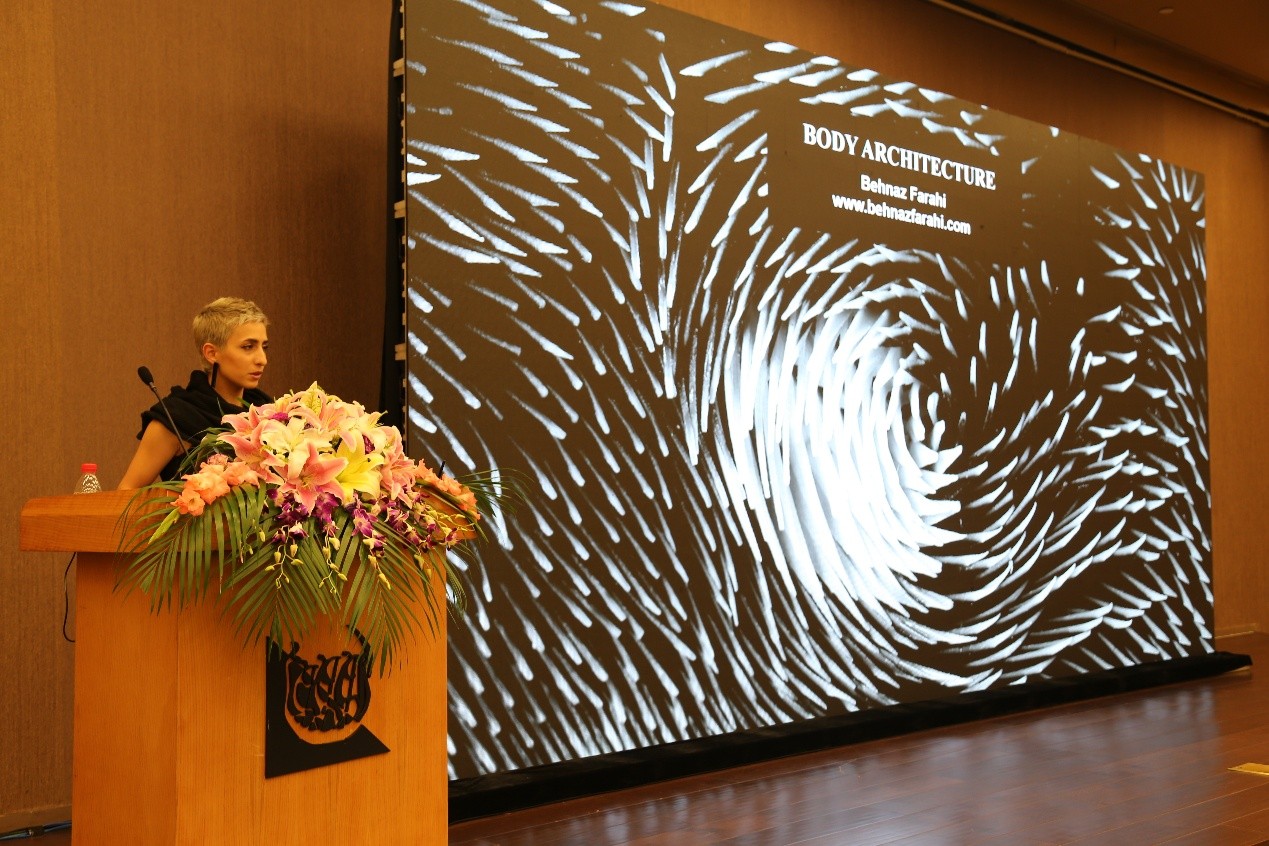
设计师和科学家Behnaz Farahi以“3D printed Interactive Body Architecture”为主题发表演讲。Behnaz Farahi是一位具有创造力的杰出设计师和科学家,她的主要研究横跨时尚,建筑和交互设计领域。她在作为建筑师的培养过程中,着力探索交互环境与人体关系的潜力。她还专注于物理计算,传感器技术,增材制造和机器人建造技术。她目前是南加州大学电影艺术学院的跨学科媒体艺术和实践的研究员,博士在读生,拥有建筑学士学位和两个硕士学位。
Behnaz介绍了自己关于交互环境与人体关系的探索,这些探索利用了设计、科技、机械以及建造之间的联系。Behnaz尝试了可以探测旁人的目光并且以类生命体的行为给予回应的交互性的3D打印服饰,并尝试了通过探测使用者的身体运动并根据此进行重新组合的装置,以及驱动3D打印螺旋的收缩以及伸展运动而形成了看起来似乎可以在身体上爬行的、像在呼吸一般的有机体。

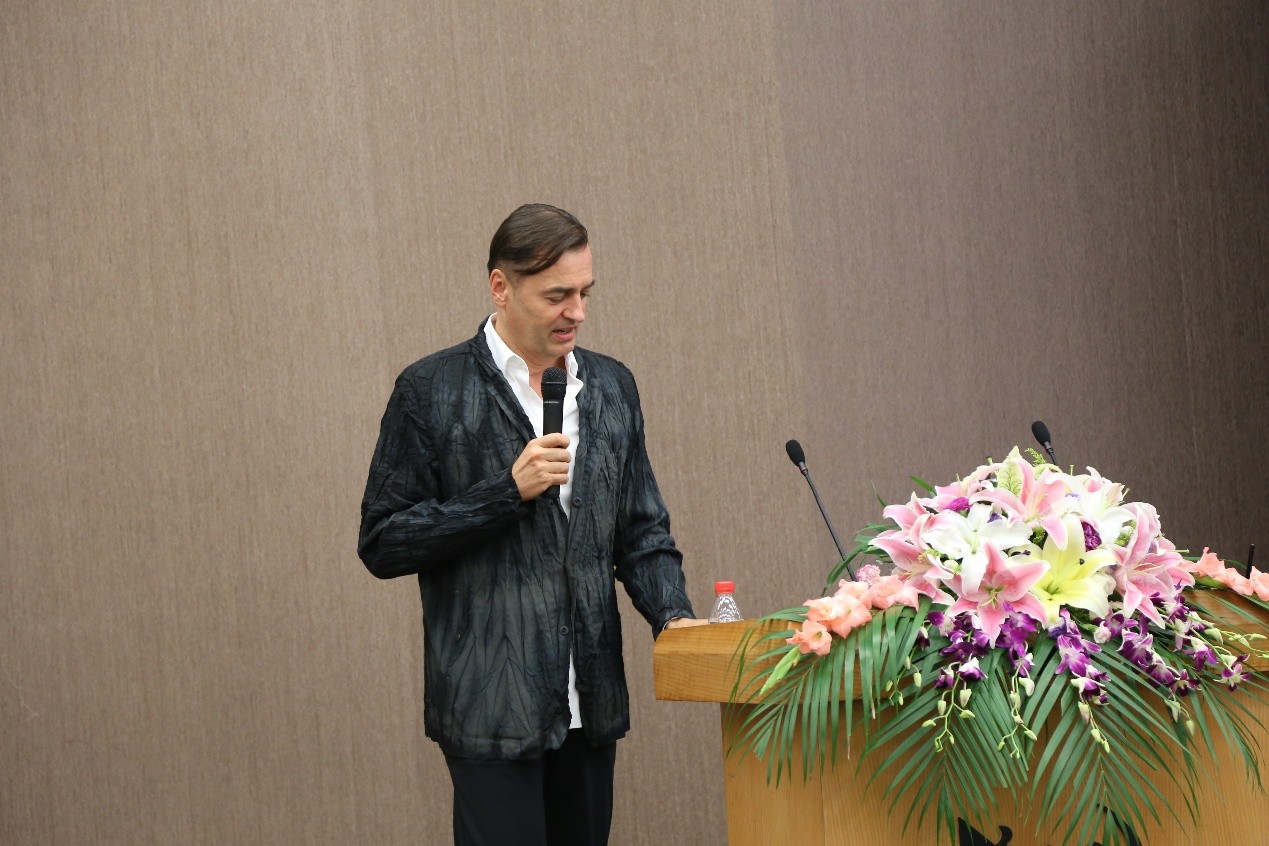
扎哈·哈迪德建筑事务所主持建筑师、合伙人Patrik Schumacher以“Tectonic Articulation in the Context of Architectural Semiology”为主题发表演讲。Patrik Schumacher是扎哈·哈迪德建筑事务所主持建筑师、合伙人;英国皇家建筑师协会成员。曾在英国,欧洲,美国多所建筑院校任教,并且是伦敦建筑联盟学校(AA)设计研究实验室(DRL)的联合主任。他也是一名理论家,专注于参数化主义设计。在舒马赫先生看来,利用算法、计算机设计和新型材料塑造建筑物的参数化主义是后现代主义的继承者。
Patrik认为,建筑/建构的形式是多功能的,需要根据两组不同的功能标准进行选择:基于物理性能的技术功能和基于交流性能的社会功能,这两个标准之间应该相互契合,可理解性涉及两个方面:感知易处理性/触觉性和语义信息,我们需要区分现象学表达和语义表达。建构的概念是由于建筑技术与构件接合之间的关系而出现,在建构领域,许多建筑理论家阐释建筑的本质,技术的有效形态在变化的历史进程中成为一种有意识的设计策略。建构的衔接根据现象学和语义学的要求从所有技术上可行的解决方案中选择最终解决方案,而随着城市复杂性和密度的增加,有效的建构衔接越来越重要。




“上海数字未来”展览于7月1日下午在同济大学建筑与城市规划学院开幕,展览将一直持续到9月30日,欢迎全校师生和社会各界人士前往参观。
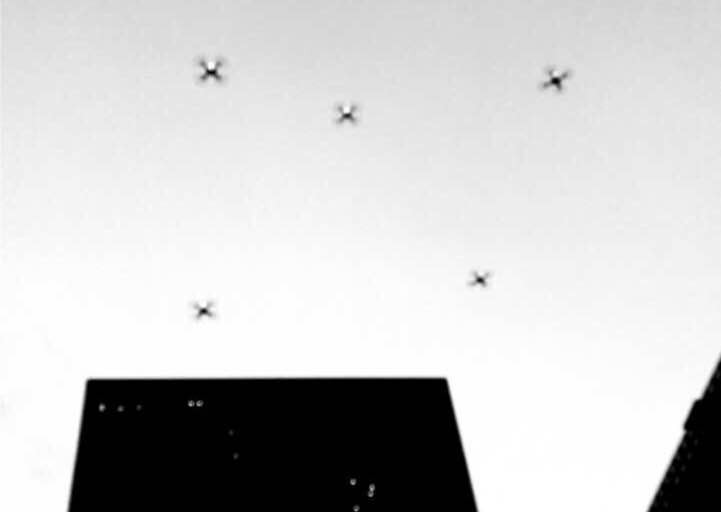
7月1日下午1:30,建造工作营成果汇报在同济大学建筑与城市规划学院B楼钟庭报告厅举行,工作营11个小组进行了成果汇报,并由各组的指导导师为小组成员颁发了结业证,同时,每个小组各选出一名优秀学员。成果汇报结束后,全体成员前往C楼地下展厅,室外展出的全球第一组3D打印步行桥吸引了众多人的目光,3D打印的小桥和大桥的跨度分别达到4m和11m,来自第4小组的无人机群引得大家的围观拍照。之后,在C楼地下展厅,同济大学建筑与城市规划学院院长李振宇为展览开幕发表致辞,袁烽教授主持了“上海数字未来”展览开幕,Patrik Schumacher、Philippe Block、Matias Del Compo、Behnaz Farahi、Biayna Bogosian、渡边淳、黄蔚欣、王文栋、孙澄宇、臧伟、Steven Ma等嘉宾发表讲话。



本次活动由上海建筑数字建筑工程技术研究中心、同济大学建筑与城市规划学院以及同济大学建筑设计研究院(集团)有限公司联合主办;由中国数字建筑设计专业委员会(DADA)、Fab-Union和中国高等学校建筑学科专业指导委员会-建筑数字技术教学工作委员会协办;由库卡机器人(上海)有限公司、昆仑绿建、异型数控营造、3D SYSTEMS、ARUP、置景(上海)科技有限公司、Association for Robots in Architecture特别赞助;同时,《建筑学报》《世界建筑》《时代建筑》《建筑师》《新建筑》《城市建筑》《建筑技艺》等多家媒体为本次活动提供支持。

主办方同济大学建筑与城市规划学院袁烽教授邀请到了来自全球高校的8位优秀的导师,并有8台机器人、2台CNC计算机数字控制机床、5台无人机、UWB室内定位设备、热成像仪和多台3D打印机的设备支持。今年暑期工作营有近300名学员报名,组委会从众多的报名者中根据志愿情况挑选出来146名学员,他们分别来自16所海外和39所国内共55所国内外高校以及12所建筑设计机构。其中国际学员包括来自南加州建筑学院(SCI-ARC)、建筑联盟学院(AA)、加州大学伯克利分校(University of California, Berkeley)、伦敦大学学院(UCL)、法尔茅斯大学(Falmouth University)等海外先锋院校,及来自同济大学、清华大学、东南大学、华南理工大学、天津大学、浙江大学等在内的国内高校的教师、硕博研究生及本科生。

本次活动以“可视化与物质化”为主题,邀请多位国际著名学者、建筑师讨论数字化未来的可能方向。从模拟、虚拟到增强现实,与日益发展的数字建造技术之间正在对立、交互还是合作融合?我们期望从建筑哲学、理论与实践的诸多视角讨论这个议题。对于建筑学、结构工程学、材料学等传统学科来说,在这个激变的时代,本次会议立足历史与当下,展望未来,是一个探讨学科边界与发展的绝佳时机。
下面将对各组工作营的成果进行介绍:
1. Rhino VAULT
指导团队:Philippe BLOCK教授(苏黎世联邦理工学院建筑学技术学院(ETH),瑞士国家技术研究中心(NCCR)主任)
Shajay BHOOSHAN(扎哈·哈迪德建筑事务所(ZHA | CODE))
助教:周轶凡,张立名
学生团队:孟宪川,方志浩,陆垚,王宇泽,张春祺,姚稼澍,徐鳴亞,刘凌灵,赵琦,李明亮,蒲昊旻,周保林,杨灵运,杨文倩,王建桥,左颂文,杜杰,俞洲
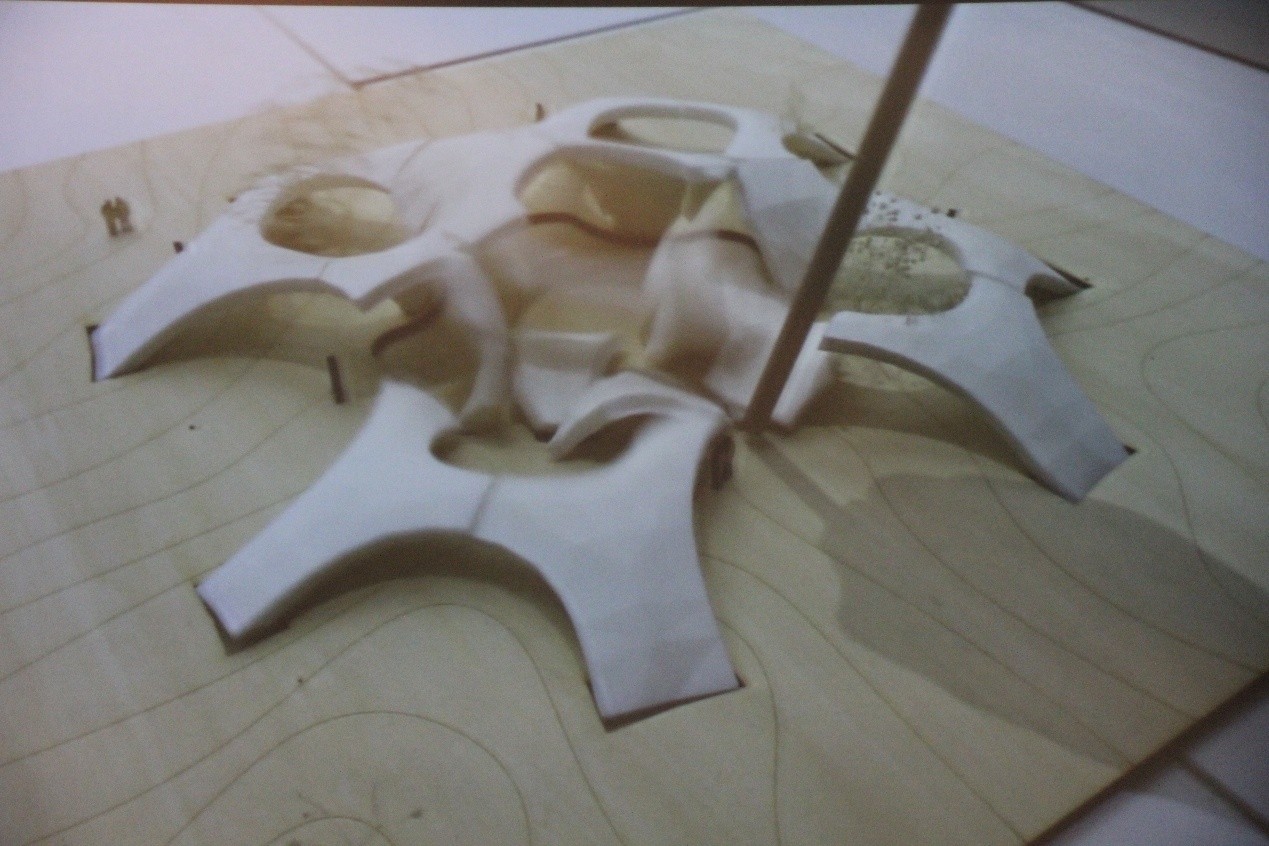
本组工作营由苏黎世联邦理工学院(ETH)Philippe Block研究组与扎哈·哈迪德数字设计研究小组联合教学的。以机器人3D黏土打印为基础,从结构信息建模,转换为打印路径,最终实现实体建造,打印完成的拱石组件将用于搭建成更大的拱形结构。学生使用RhinoVAULT插件来找形与结构优化分析,同时操作3D陶土打印与烧制,最终组装成结构优化的拱形装置。
It’s a joint workshop/ collaboration between the Block Research Group at ETH Zurich and the Computation and Design group at Zaha Hadid Architects.Based on robotic 3D printing of clay, a joint research project in which we focus on structurally informed modelling of such objects and processes.Printed ceramic voussoirs/bricks to assembly a larg(er) self-supporting cellular or shell structure, as a formwork . Students use RhinoVAULT plugin to do forming finding and structure optimization research. Also be able to operate robotic clay printing & firing and then assemble printed brick into a shell structure.


2. 机器人木缝纫
指导团队:Achim MENGES教授
Martín ALVAREZ(德国斯图加特大学计算设计学院)
Erik Eugenio Martinez Parachini(德国Haas Cook Zemmrich STUDIO2050)
助教:胡雨辰,柴华
学生团队:赵阳臣,王航,王博伦,孙缘,秦鹏,杨扬,赵明书,李江宁,黄亮博,李胤赜,江原,陈思佳,武依,焦智恒,曹仪,刘永康,高博
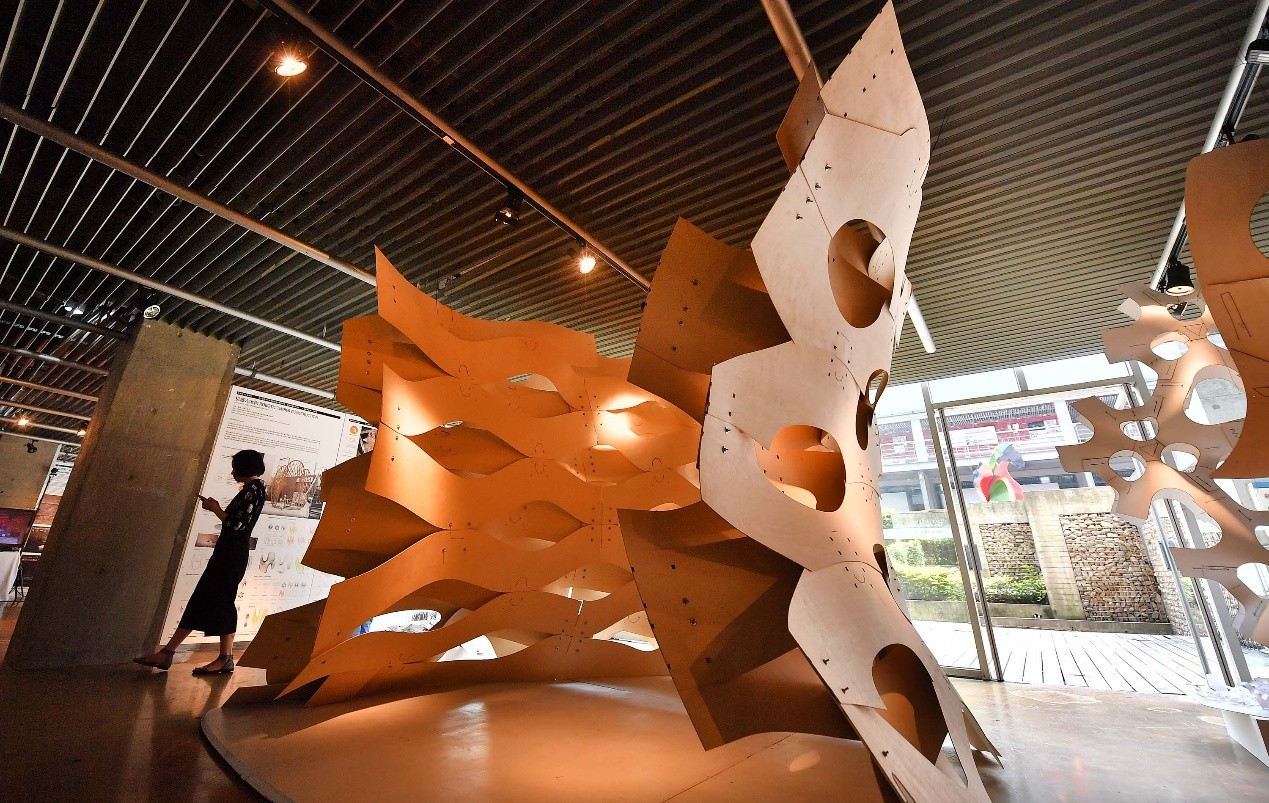
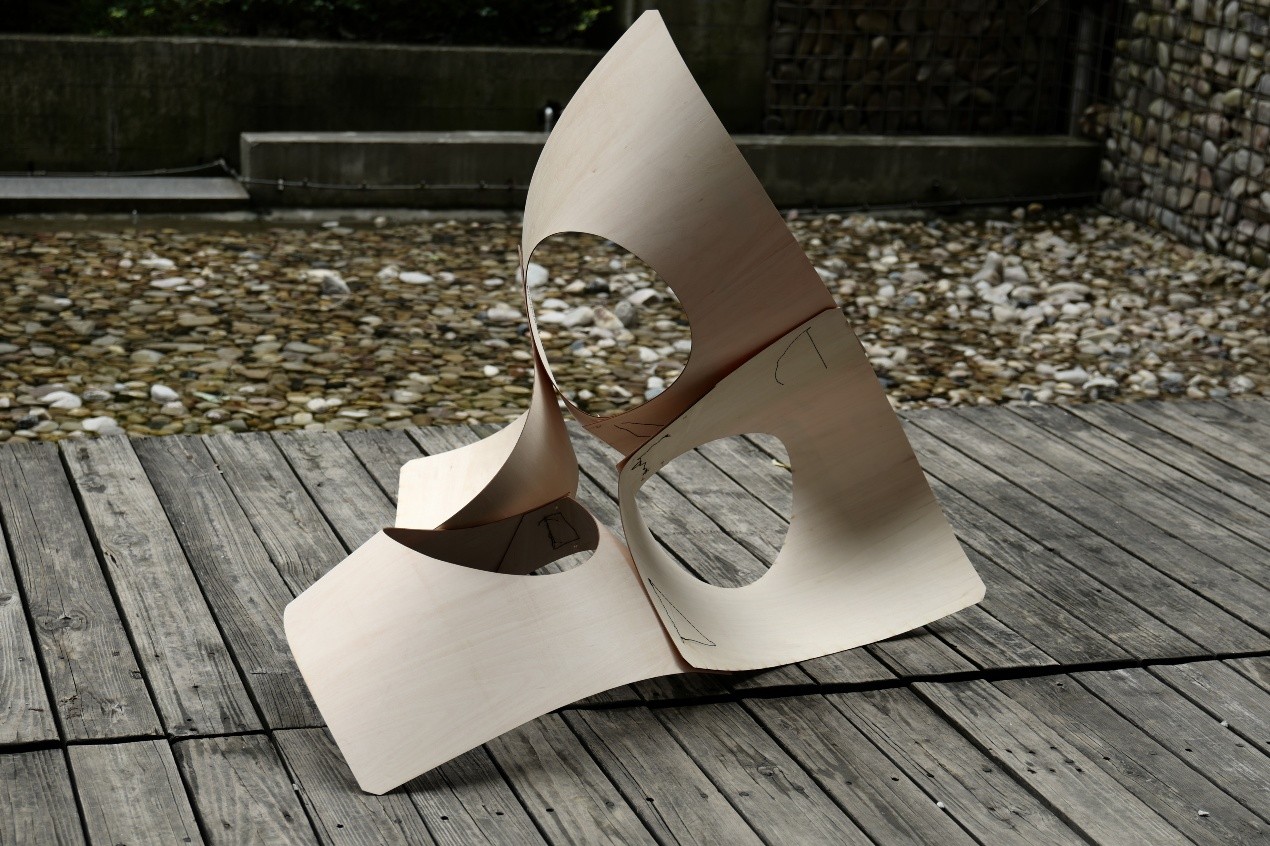
本组工作营探讨了基于机器人木材缝合的数字化工艺,通过缝纫将平面胶合板直接连接形成复杂的三维自由形状。三种基于机器人木缝纫技术开展的木材弹性弯曲缝合的研究被平行地进行:学生个体通过探索纺织图案和与纺织技术,创建了薄片材料的材料系统,并期望可以将其扩展到如木材之类的更厚的材料之上。在个体研究的基础上,学生分团队选择了一些材料系统原型来进行更大尺度的材料实验,以创建能够创建封闭单元体的构造策略,以期在建筑尺度进行建造。最终,木材建成的大尺度的建构范本,全面展示了木缝纫系统的性能,并为机器人自动化缝制系统做了很好的实证研究。
The workshop explore digital fabrication concepts for Robotic Timber Sewn assemblies where flat sheets of plywood are turned into complex 3-dimensional free-form shapes by using sewing as a straight forward connection. Three investigations in elastically bent robotically sewn wood were developed in parallel trajectories. Students individually explored textile patterning and fabric manipulation techniques to create material systems in thin sheet material, in an effort to scale up into thicker materials such as wood. Student groups developed a selection of these material systems in large scale segments to create a tectonic strategy capable of creating enclosure, these prototypes were fabricated aiming to be built at an architectural scale. A large scale demonstrator was constructed in wood to showcase the capabilites of the system in full scale, and to showcase the automated robotic sewing system.



3. 3D打印的身体建筑学
指导团队:Behnaz FARAHI(南加州大学)
教授(欧洲研究生院,同济大学建筑与城市规划学院客座教授)
助教:赵耀,陈哲文
学生团队:Anna Nikolaidou,赖坚,程雨阳,李佳枫,江酉玥 ,曾绍庭,梁丹,常雪石,罗劬,马诗琪,陈铭家,杨柳,崔强,汪宇宸,Dascia Kryvko,刘迪
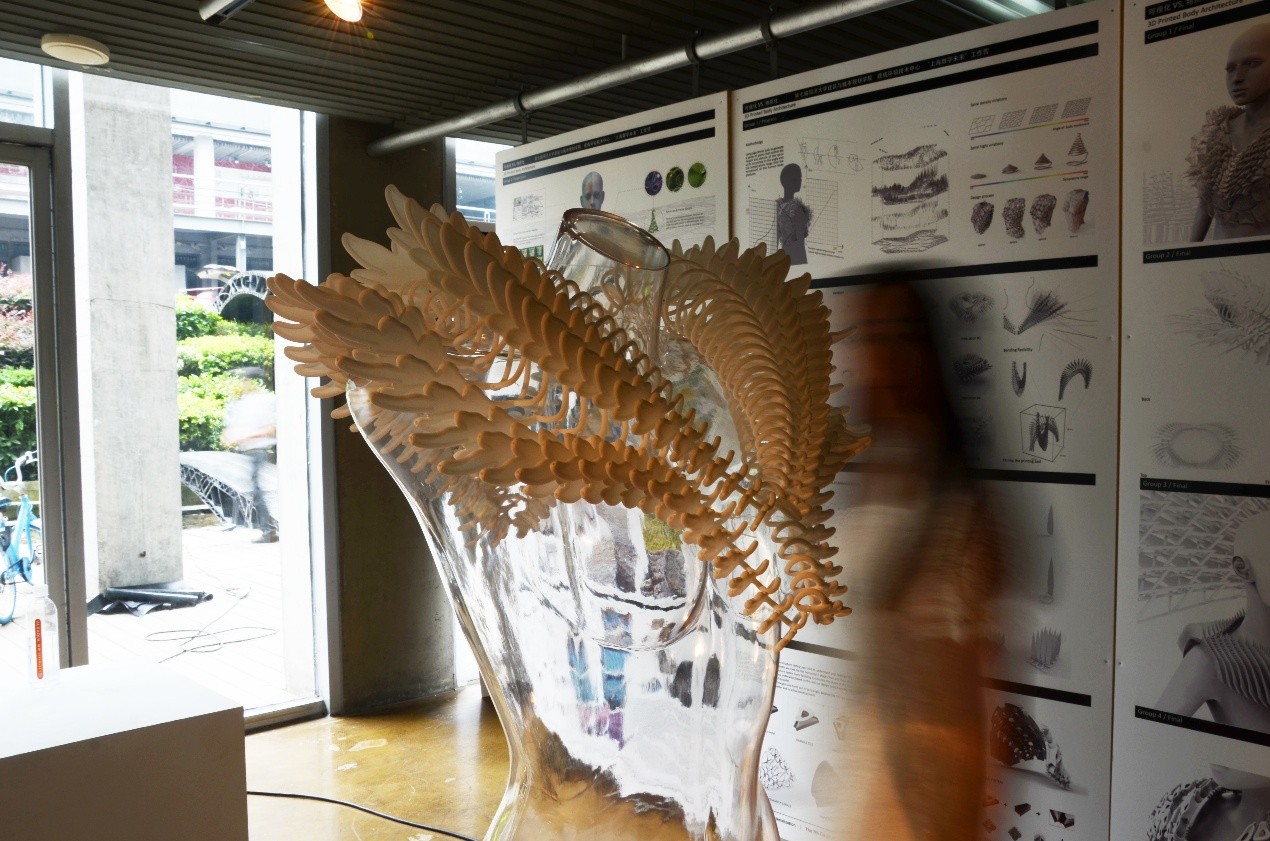
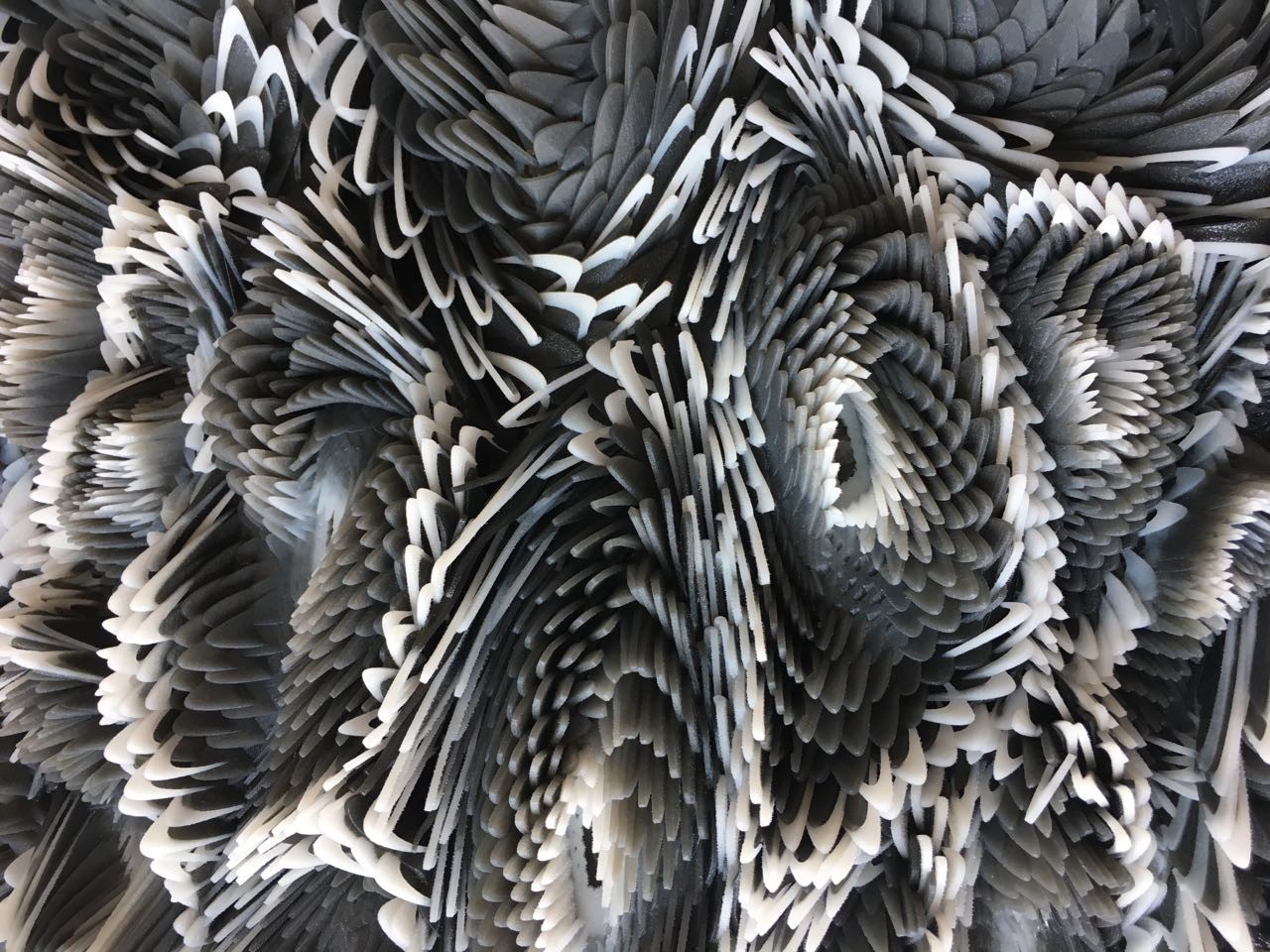
关于身体和建筑的关系研究已有悠久的历史,从维特鲁威之前人们就尝试着把建筑比例与人体尺度进行关联,到了现代身体与建筑的关系已经发展到有趣的地步:建筑师们涉足时尚界,设计一些精美的3D打印服饰。工作营强调两个初始问题。第一个是通过研究自然模式—例如生长、生枝,以及填充等—我们将会在自然中学习动态的表现方式,根据Grasshopper的教程,学生能够生成来自于生物启发下的模式,学习这些几何的背后的用意是为了能够理解动态的材料表现方式,如直线或者曲线运动;第二,将人体例如皮肤张力、肌肉运动、力的分配等作为这类形式的研究内容,我们将会尝试把生物启发下的几何模式与人体性能表现进行结合。最终我们关注3D打印过程,它的目的是去设计以及打印“身体建筑”——3D打印大衣将会与人体的肌肉与运动进行关联,使用尼龙SLS材料打印技术生产硬性的物件。但是,通过对不同材料的理解运用会使得我们可以生产出富有弹性的结构体系。
The relationship between the body and architecture has a long history. From Vitruvius onwards there have been attempts to relate buildings to the proportions of the human figure. More recently the connection between the body and architecture has developed into an interest in the fashion industry among architects producing some exquisitely designed 3D printed clothing.The workshop addresses two initial issues. Firstly, by looking at natural patterns in nature - such as patterns of growth, branching and packing – we will study dynamic behaviors in nature. Following some initial tutorials in Grasshopper, students will be able to generate bio-inspired patterns. The intention behind studying these geometries is to understand dynamic material behaviors such as linear or curvilinear movements. Secondly, by looking at the human body as a context for these forms we will reflect on how the body itself operates. By studying the mechanical and physical properties of the human body - skin tension, muscle movement, force distribution, and so on - we will attempt to relate the bio-inspired patterns to the geometries and behaviors of the human body.Finally we move on to the 3D printing process itself. The intention is to design and print ‘Body Architectures’ – 3D printed garments that relate to the scale and movement of the human body. We use nylon SLS printing technology that normally produces rigid objects. However, by understanding differentiated material distribution we also be able to produce flexible structures.




4. 无人机群感应的城市环境
指导团队:Biayna BOGOSIAN(南加州大学)
臧伟 (同济大学数字设计研究中心(DDRC))
助教:周奕霖,郭喆,齐冀
学生团队:董潇晓,吴晓涵,郭翰宸,杨慧,胡颖,季嘉为,王逸聪,张天翔,高申,袁靓,容志毅,杜巧,韩旭,李子璇
本课程利用传感器和可视化技术对城市环境进行航空测绘,旨在介绍城市环境测绘的理论和技术框架,让参与者理解城市参数的影响。借助无人机群搭载的传感器,在城市上空对城市进行数字环境的检测和建设;通过大数据学习可以将无人机群变成一个有“智能”的团队,为我们传达全新的时空信息;由此我们可以了解到诸多以日常视角无法感知到的影响城市空间的参数,例如建筑形态,植被,地形变化以及微气候等。最后利用可视化技术和工具,把原始数据进行艺术的转译,将城市环境映射到建筑设计,艺术创作以及视觉表达中。
This course focuses on spatio-temporal aerial mapping of urban environments, with emphasis on field application of sensors and visualization technologies. This course aims to introduce the participants to the theoretical and technical framework of urban environmental mapping, to understand the influence of urban parameters. This course focuses on spatio-temporal aerial mapping of urban environments, with emphasis on field application of sensors and visualization technologies. This courseaims to introduce the participants to the theoretical and technical framework of urban environmental mapping, to understand the influence of urban parameters such as,building morphology, vegetation, or topographical variations in urban microclimates. We will use the campus of the Tongji University as the case study of our investigations,and will operate drones equipped with sensors and cameras to document the environment. Through lectures and hands-on exercises, participants will employ variouscustom toolsets to visualize and analyze the collected data against GIS databases in QGIS and Rhino3D/Grasshopper environments. This course will culminate in composition and presentation of videos that will demonstrate the students’ workflows and analysis.
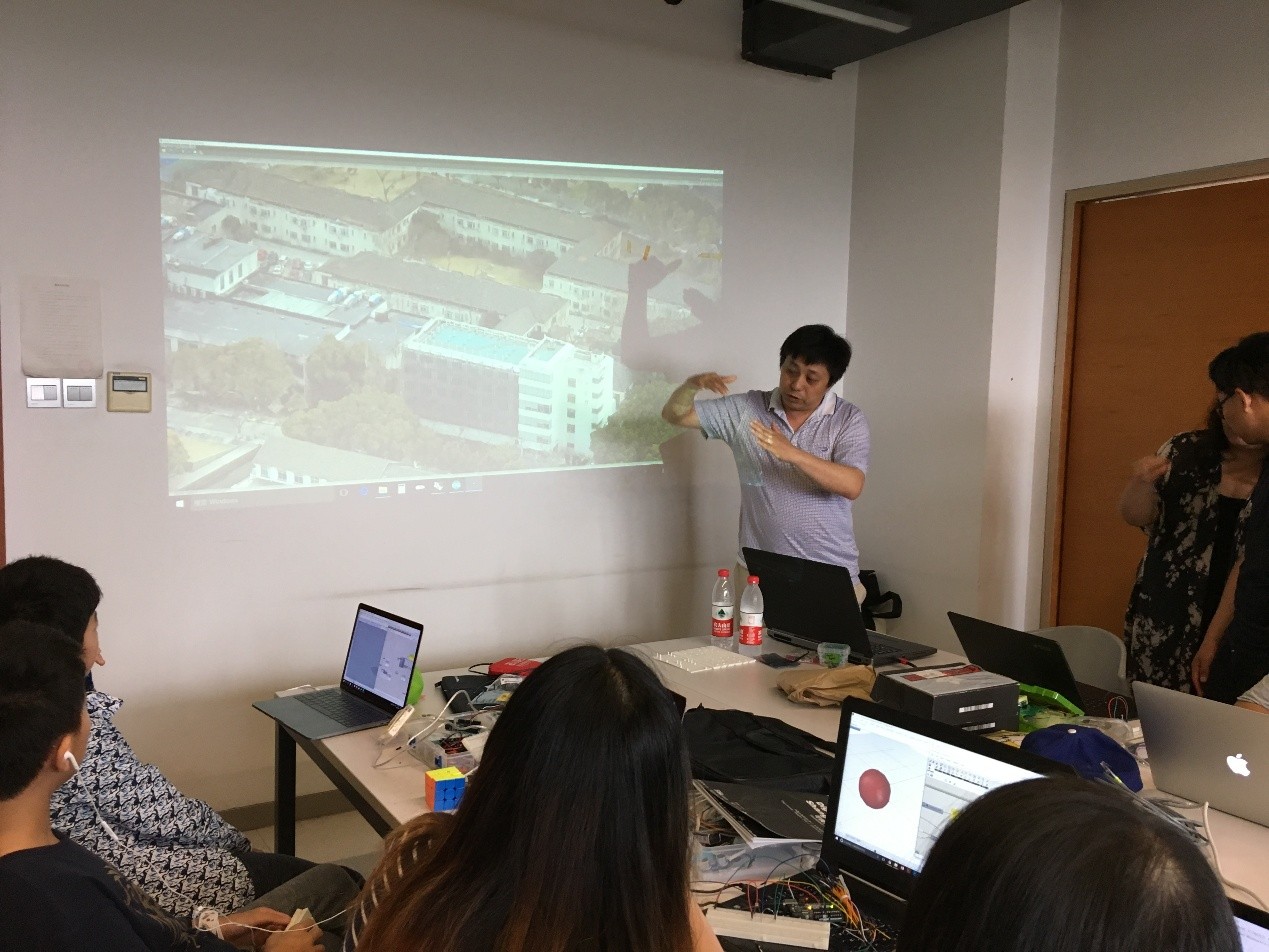




6. 超薄纸板大跨建构
指导团队:王祥博士(德国达姆斯塔特工业大学)
助教:王祥
学生团队:韩旭,林誉婷,官诗菡,刘江德,吴薇,郭志滨,张力行,聂家鑫,段晓天,白雪,周静微,史学鹏,李至,何薇,葛康宁,徐赫言
本课程利用超薄板材建造一个小型的壳体,来探讨和研究一种新的针对材料结构性能的壳体结构概念设计方法;同时,课程也回顾了自上世纪到近期的壳体结构发展过程以及其设计方法的转变,进而探讨一种基于材料的性能化设计方法;最后,课程提出一种新的壳体结构形态学设计思路,并探讨基于材料的形态学设计方法。
通过学习设计过程,教授学员壳体找形的理论及软件模拟过程。同时,通过建造的过程,完成对于结构细部构造的理解和设计优化。最终,每位参与学员使用本工作营的设计工具,独立完成一个个性化的壳体形态设计方案。
This workshop aims to explore and study a new conceptual design method for the shell structure with thin sheet materials based on the materials’ structural behavior. A small free-form shell is built finally as a demonstrator for the structural concept. At the same time, the workshop also review the development of shell structures and its changes in structural typology from the last century to the recent years. Through the discussion, a material-performance-based design method is introduced as a design methodology. Finally, the course present a new design logic of the structure of the shell and explore the morphological design method based on the specific materials.Through the study of the design process, students learn the form-finding methods of shell structures and the software simulation process. At the same time, through the construction process of the structure, the consideration and optimization of the construction details also be understood. In the end, each participant also use the design tool of the workshop to complete a personalized shell design.
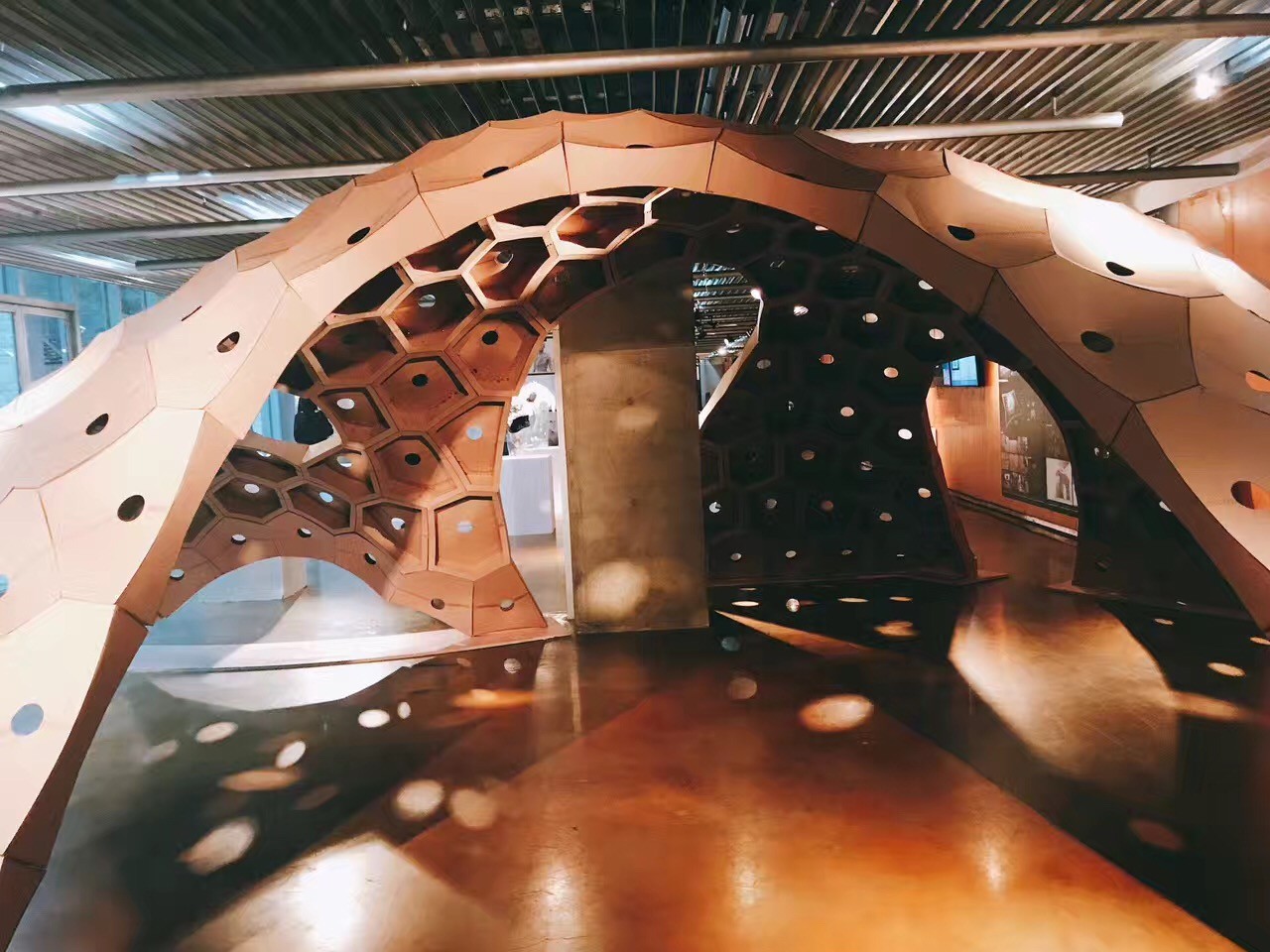
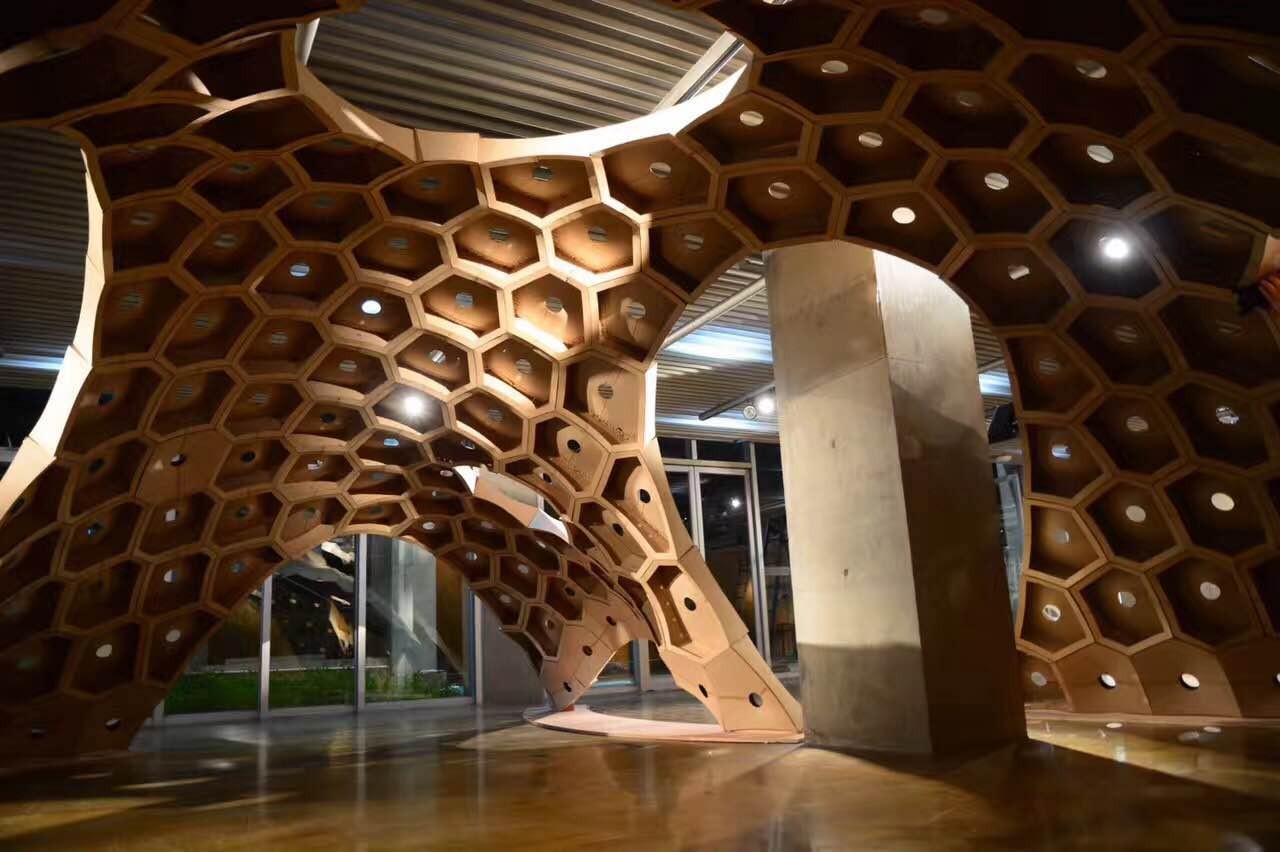




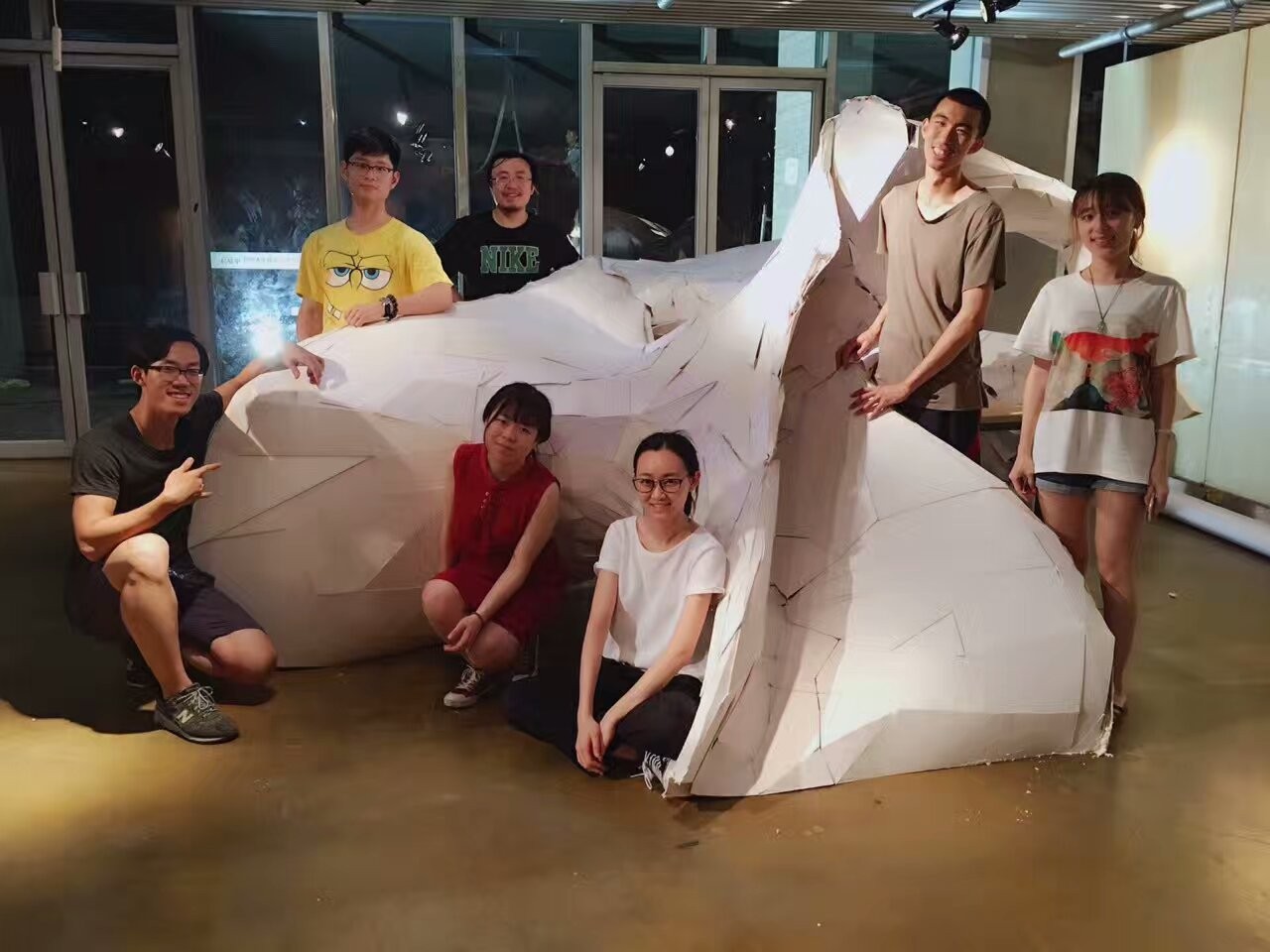
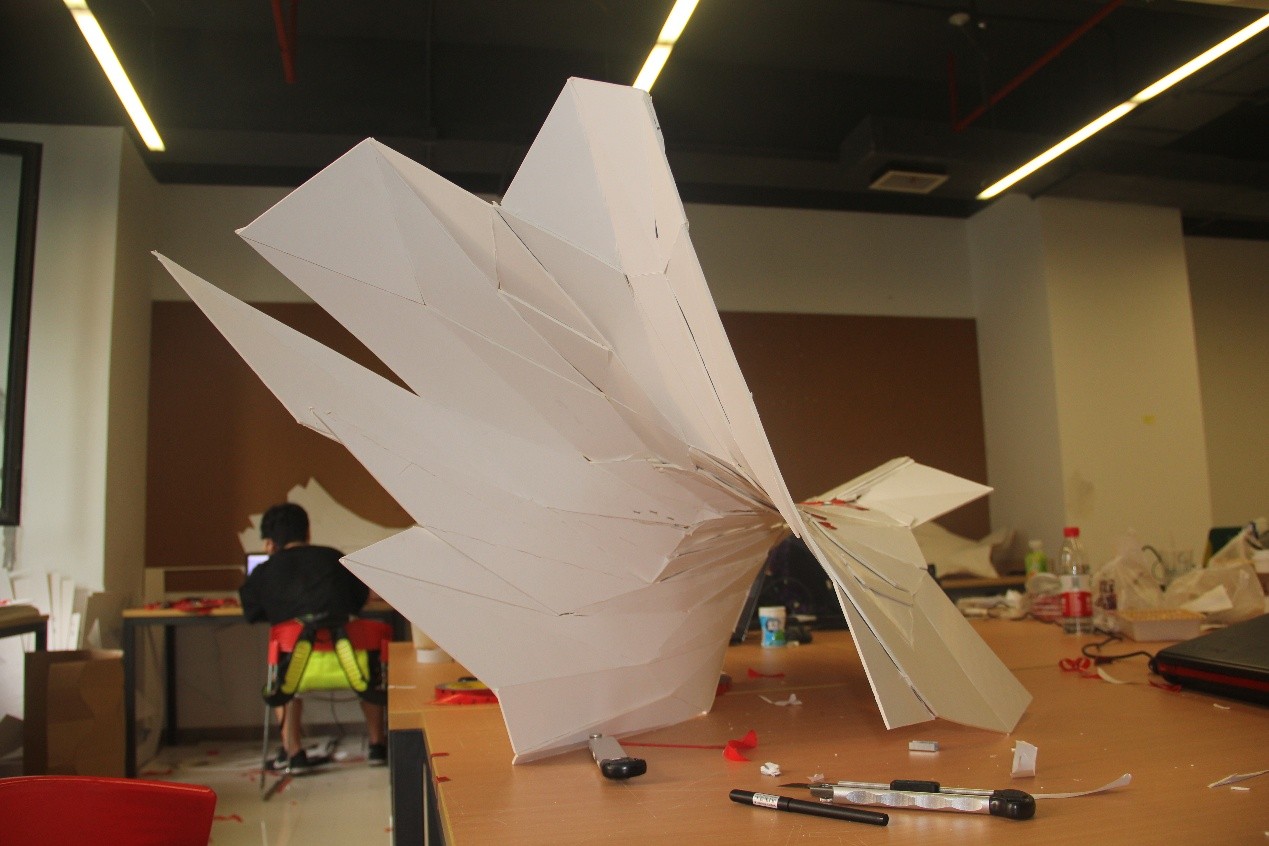
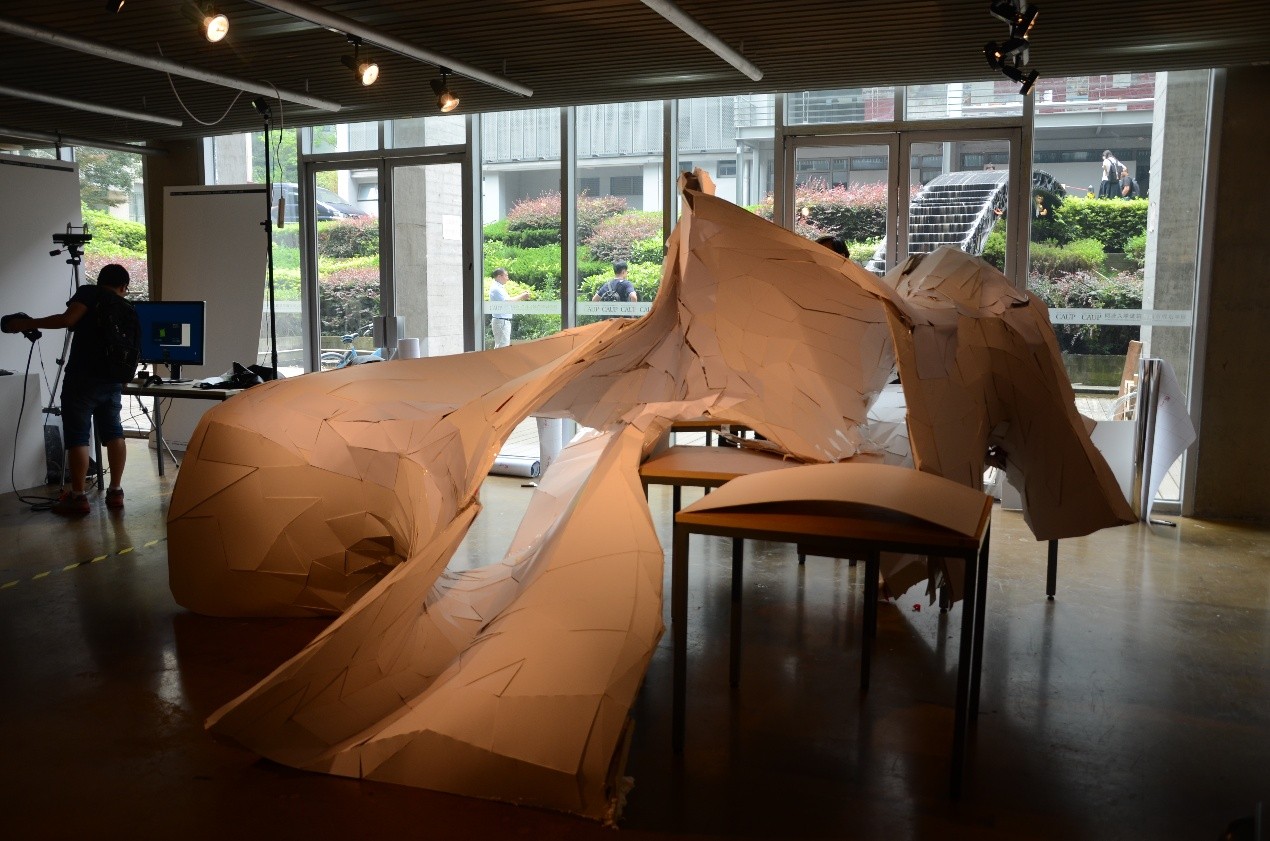
7. 数字化折纸编程
指导团队:王文栋(中央美术学院)
助教:张啸
学生团队:周嘉伦,佟天泽,张婷,周丹妮,谢雨帆,李晓琳,朱玉,李虹娇,李孟轩,赵珂
参数化折纸将复杂的几何形与空间变量进行综合、转化、变形,从而对空间表达进行新的尝试,最终成果为大尺度空间薄板折叠装置。课程通过教授多种数字、编程、计算等参数化方法进行方案设计,使用Rhino并进行Rhinoscript编程设计。该研究把复杂几何形式的各种变化属性与实物模型相结合,激发学生的空间想象力,借助纸这一媒介,创造新的形式语言。
Scripting “Paper Fold” can synthesize, transform and deform complex geometric shapes and variable space, thus it gives a new attempt for spatial ex




8. 虚拟现实:从诗歌到场所的转换
指导团队:孙澄宇副教授(同济大学建筑与城市规划学院)
陈达博(英国皇家艺术学院与帝国理工双硕士,浪走科技创始人)
杰夫・卢明斯(美国VR科技公司Worldviz资深工程师,全球技术支持负责人)
宋晓宇(光辉城市CEO)
助教:许迪琼
学生团队:朱元双,闫力,韩果均,张志诚,于晴,何幸鑫,戴巍,谢云玲,冯源,吕翰林,许潇文,王佳欣,李晗玥,熊沁,张哲远,李伟成
随着VR技术不断深入我们的生活,建筑师也会有关于VR的不同想法,本课程通过一个对文字抽象体—诗歌的可视化场所转译,为创作者提供多种探索VR意义的可能,这里的场所包含空间与其中活动的人,它可以用来详细描述诗歌的意境,或者只是配合这种意境的表达,甚或表达对于意境的不同看法……工作营以2-3个小组为单位,每个小组完成一组诗歌与场所的转译设计,包括模型制作、空间搭建、人物表演摄制。通过在虚拟空间的这一创作过程,在暂时放下建筑材料、构造、结构等因素的束缚厚,尝试完全通过场所感去表达设计用意,使得成果可以像任何一件艺术品那样被欣赏,并借由诗歌的力量来触动体验者的心弦。
Today, we see more and more VR technology being used in our daily life, this has brought inspirations to architects, too. This workshop explores the multiple meaning of VR through converting poems to virtual places.As a place in architectural context, it includes a space, people in activities, and other sensible elements such as rain. It is expected to touch the heart of visitors according to the meaning of the poem, the feeling, or any other perspectives that are related to the context. Within the given time, students join others to form teams with 2-3 people, each team complete the conversion of one poem to one virtual place, including creating the 3D model, building the space, recording the activities. Students should consider the outcome as a piece of art by fully exploring the potential of the place and expressing their meaning and feelings without needing to consider any real world or technical constraints, such as the materials, details, and structures.




9. 风洞可视化
指导团队:郑静云(FabUnion)
袁烽教授&姚佳伟博士(同济大学建筑与城市规划学院)
苏建鸿&许萌(置景(上海)科技有限公司)
学生团队:李社宸,解雅倩,王蕾,李骜,何美婷,刘功浩,冯艳玲,周锡晖,张琪,孙瑞基,李天纬,应静怡
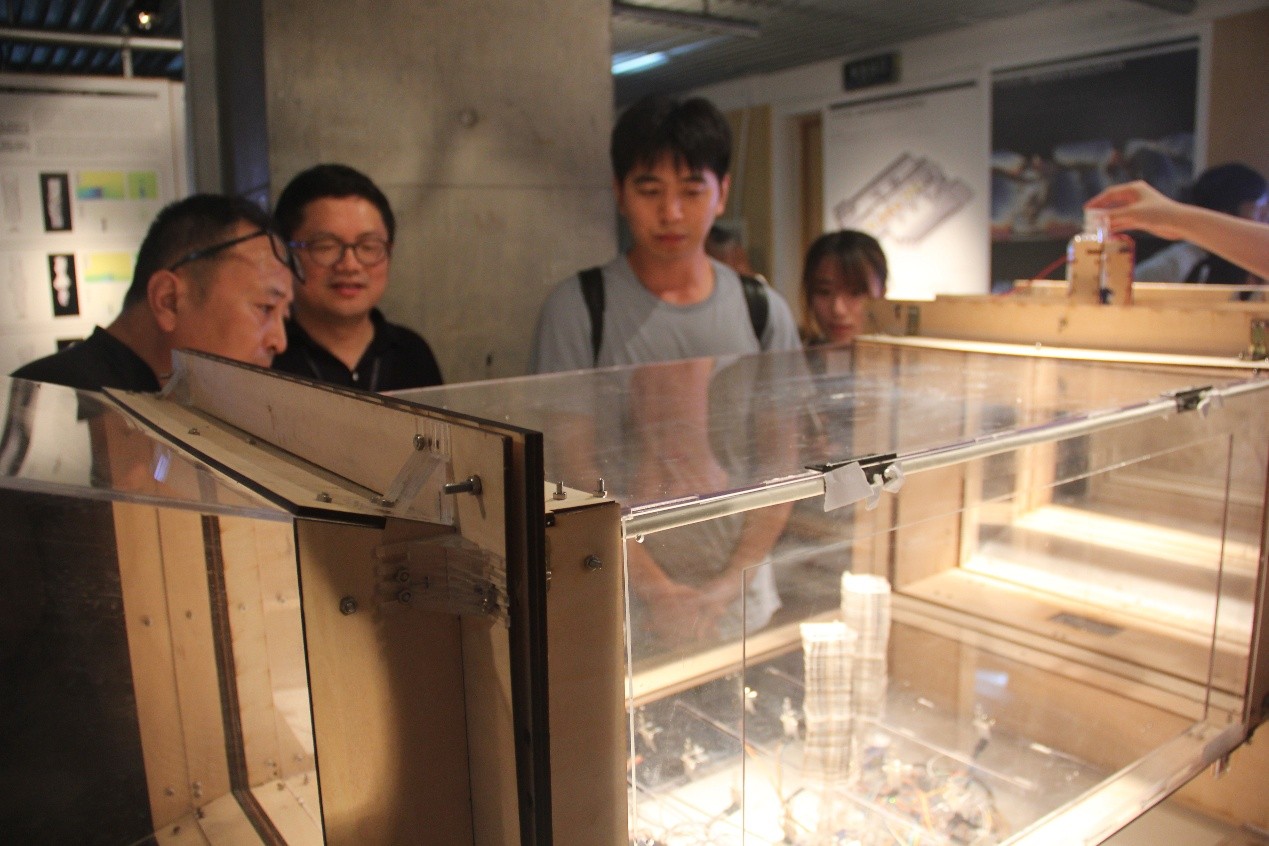
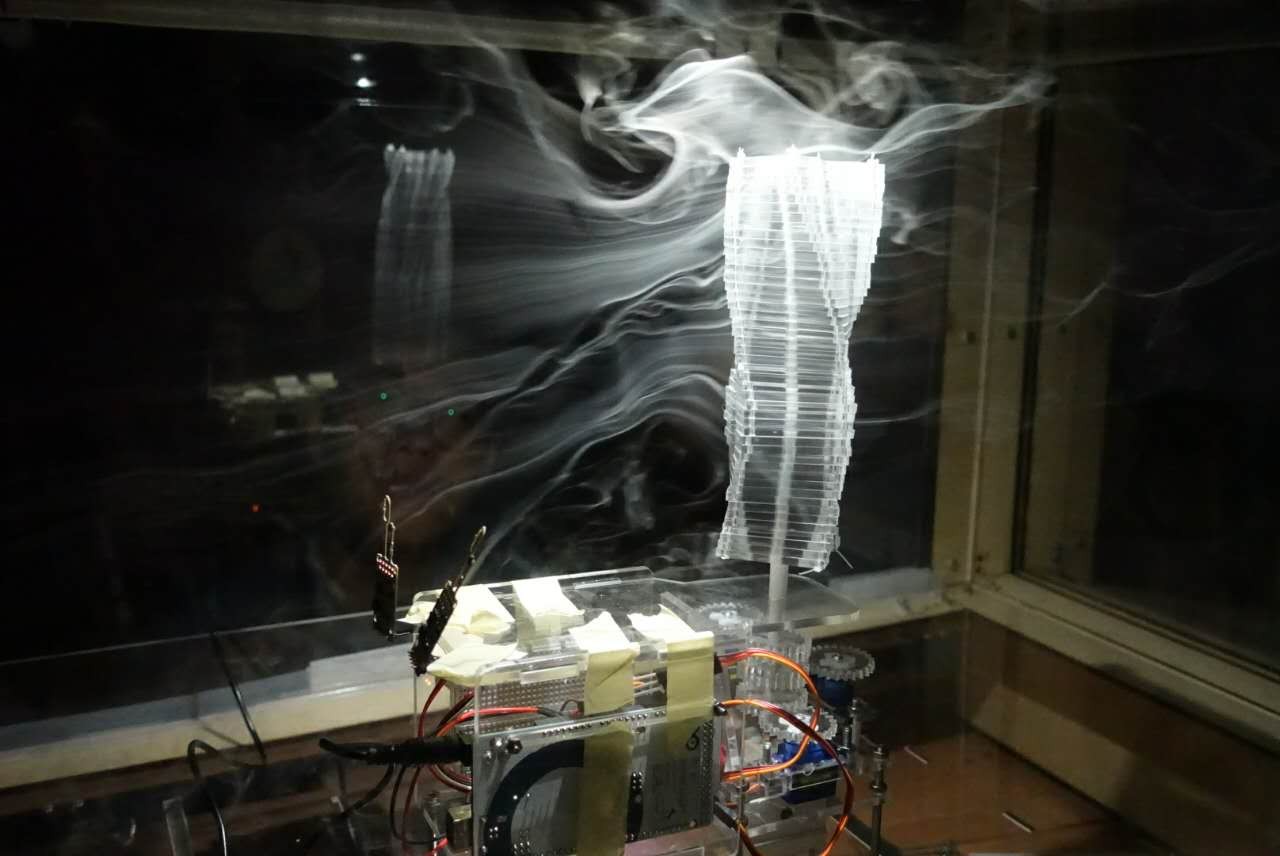
工作营旨在探讨在建筑设计初期阶段运用物理风洞及AR(增强现实)工具探索建筑形体的可能性,使环境性能成为城市与建筑生形的驱动参数。在设计初期阶段,物理风洞提供了一个直观且快速的可视化平台,可对城市建成环境或是建筑周围环境中的风、热等要素进行定性、定量的模拟测试。此外,建筑师通过互动工具建立数据可控的模型,以及矩阵排布的传感装置,将基础的建筑几何形体与风环境数据互动迭代,获得基于舒适环境数据的基础几何形体。同时,基于CFD的数字模拟,生成多点式的伪色图及流线图,结合AR技术将风环境模拟结果带入“现实”,增强可视化的空间感受。在物质化方面,利用风洞作为风环境的主要模拟工具,完成建筑形态的研究及概念设计,使风环境数据和建筑主体形体之间产生互动与反馈,在考虑舒适风速及温度的条件下,获取最终的建筑几何形态。在可视化方面,利用不同的工具对风这一不可见的要素进行研究,并将结果反映在建筑形体的调整与设计上:在物理方面,运用烟雾可视化工具,观察建筑周围的流迹线;在数字方面,基于CFD的计算结果,建立具有AR技术的APP,通过摄像头观察空气流动带来的不同影响。
This workshop aims to apply the physical wind tunnel and AR (Augmented Reality) tools to explore the possibility of building form in the early stage of architectural design, so that the environmental performance becomes the driving parameter during the design. The physical wind tunnel provides an intuitive and fast visualization platform for both qualitative and quantitative simulation of urban built environments including wind and heat environment. Therefore, the architects establish a data-controlled model through interactive equipment, as well as matrix arranged sensing devices, to iterate the basic architectural geometry and wind environment data to obtain a basic geometry according to environmental comfort index. Meanwhile, based on CFD numerical simulation, generated multi-point pseudo-color map and streamline map, integrating with AR technology from above wind environment simulation results bring in "reality" to enhance the visual experience of space and environment. In the aspect of materialization, the wind tunnel is used as the main simulation tool for wind environment, which contributes the related research and conceptual design of the building form. The interaction between the wind environment data and the building morphology is generated.Under the condition of comfortable wind speed and temperature, the final architectural geometry will be analyzed and further generated. In terms of the visualization, the use of different tools to study the invisible elements of the wind, and the results reflected in the adjustment and design of the building form: the physical aspects that relies on smoke visualization tools to observe the flow around the building; while digital aspects, based on the CFD calculation results, the establishment of AR technology with the customized APP, through the camera to observe the different phenomenon of air flow.




10. 行为可视化
指导团队:尹昊(FabUnion)
袁烽教授(同济大学建筑与城市规划学院)
学生团队:陈思宇,王梅洁,卜梅梅,周宇琪,楊兆中,朱卓晖,杜明,章一平,程韵达,魏嘉彬,马兰,景旭
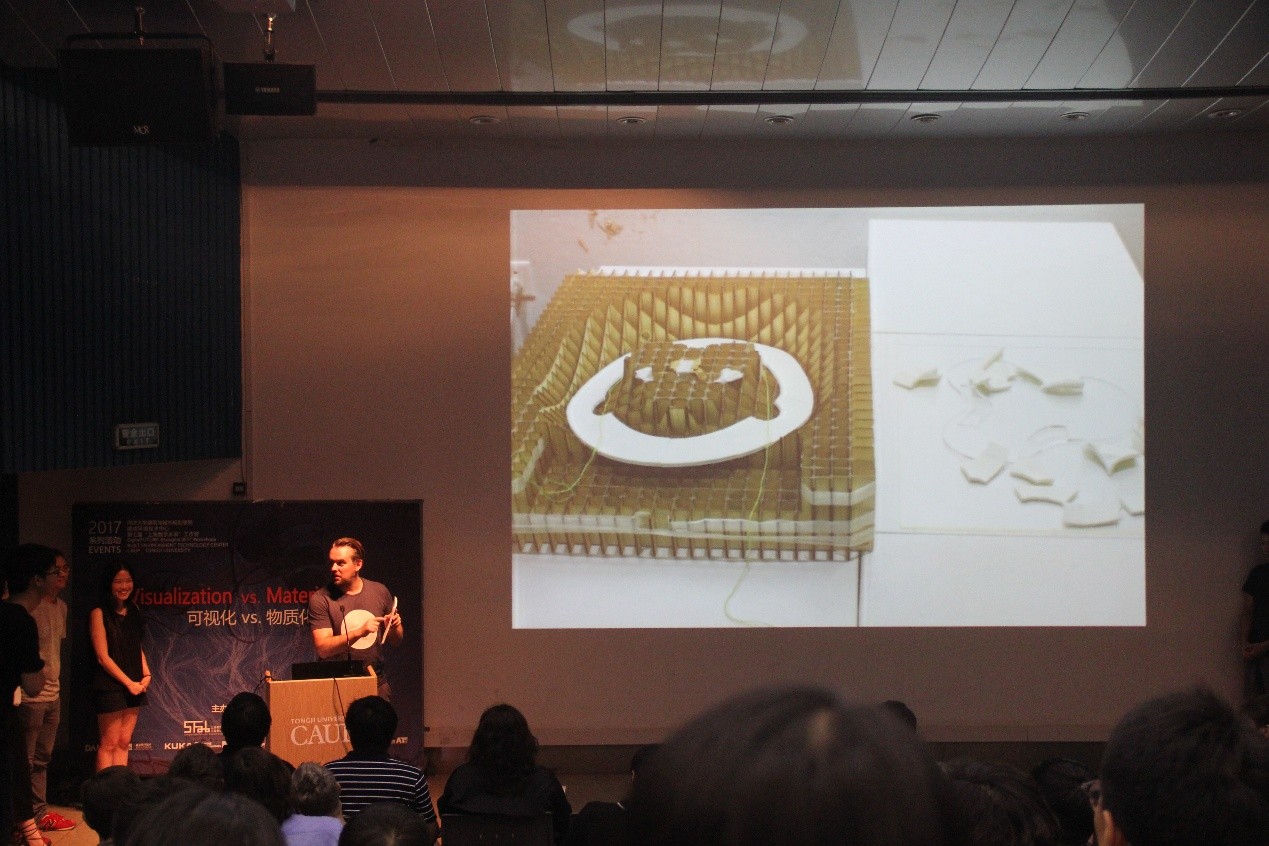
行为可视化是通过数字技术采集建筑空间中人的行为数据,并将其与空间结构进行匹配与分析,最终检测并验证空间与行为共生关系的建筑学研究方法。在数字技术的辅助下,行为数据信息得以准确而全面的收集,基于大数据而建立系统的统计分析与可视化呈现,为微观层面的建筑单体设计与整改提供方法借鉴。本项目从数据采集与分析的角度出发,采用室内定位系统来执行数据采集与行为调研的工作,通过可视化编程与统计算法提取海量的数据中的行为信息,为建筑空间中行为的精细化、定量化研究提供依据。
Based on the data acquisition and analysis, this project adopts the indoor positioning system to carry out the work of data acquisition and behavior investigation. The visualization programming and statistical algorithm are used to extract the behavior information in the massive data, which provides the basis for the refinement and quantitative research of the behavior in the building space.
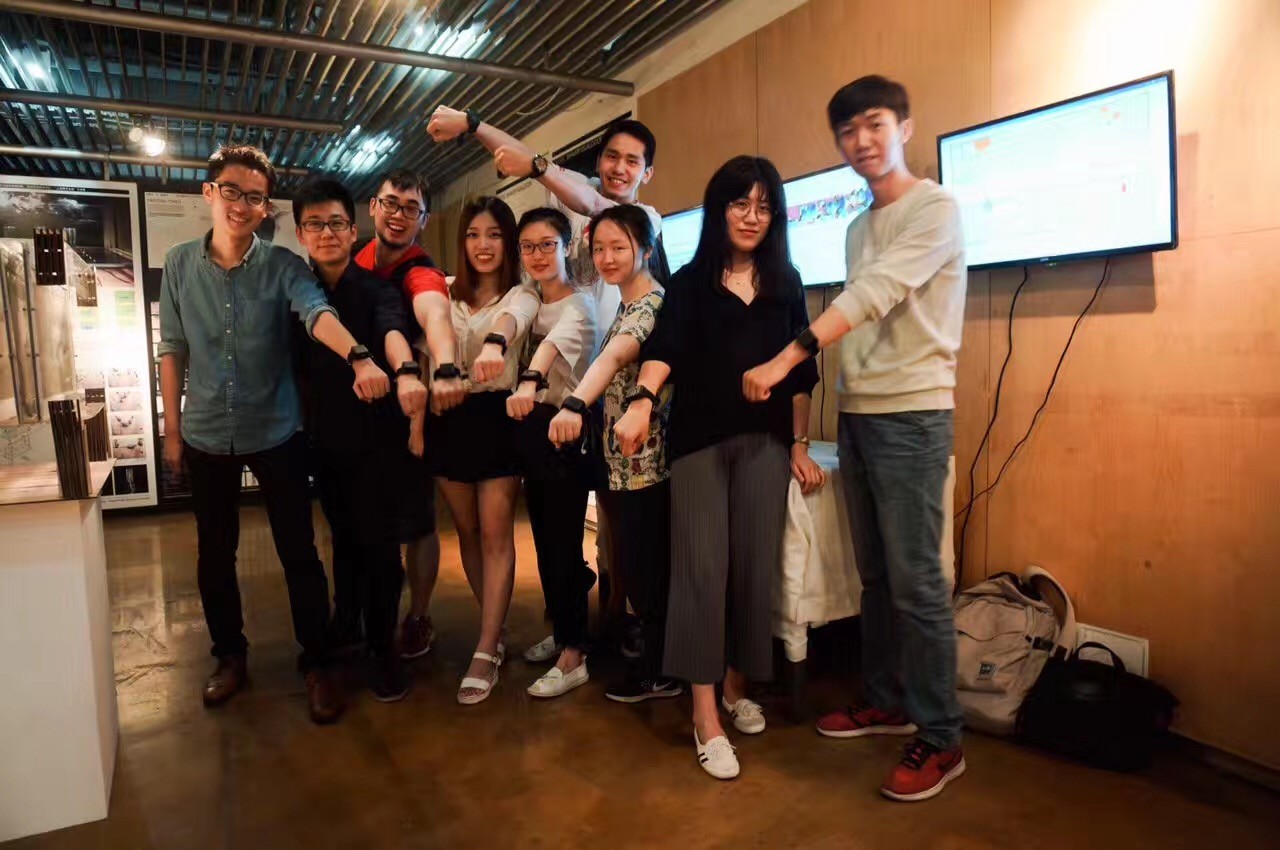




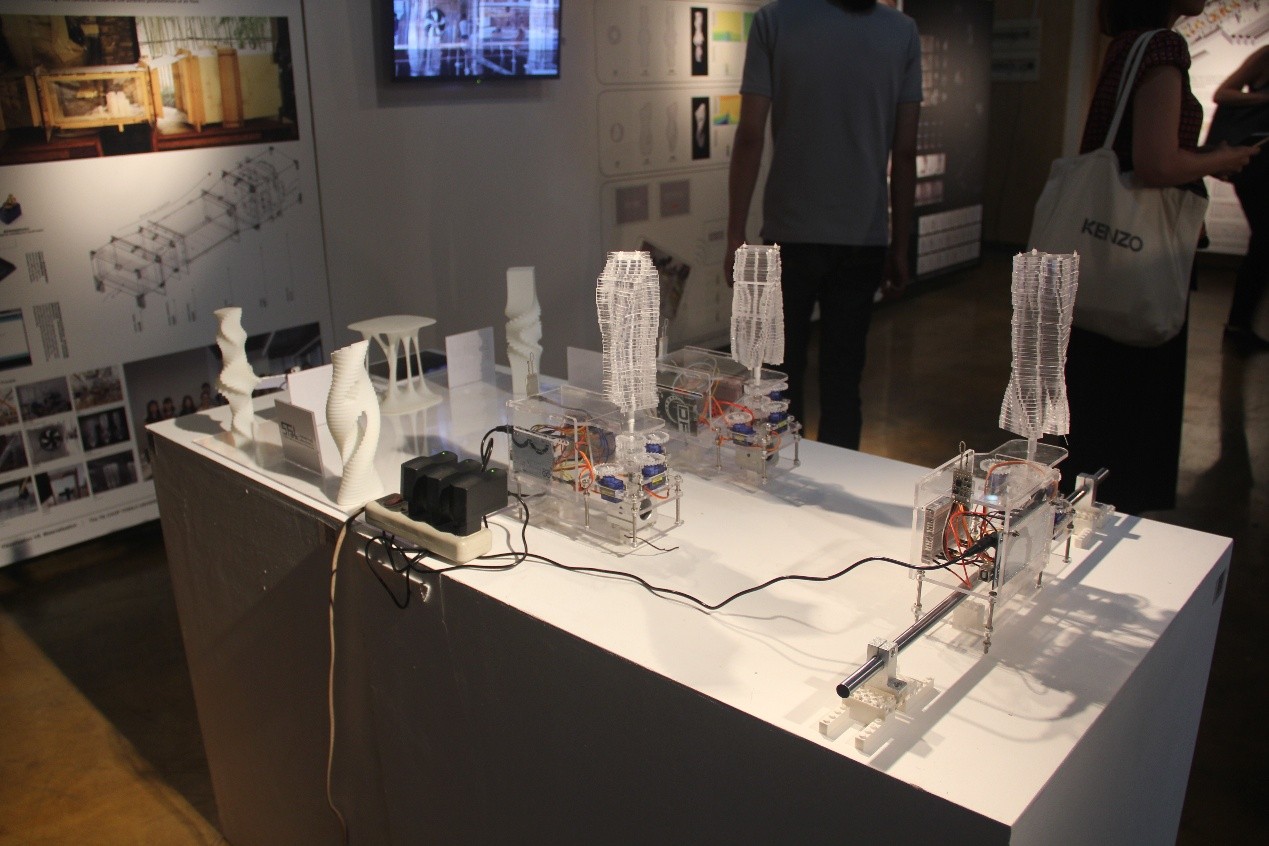
11. 机器人3D打印
指导团队:袁烽教授&孟刚副教授(同济大学建筑与城市规划学院)
张立名(FabUnion)
学生团队:陈哲文,方志浩,郑少凡,吴雨,林辰彻,Frank
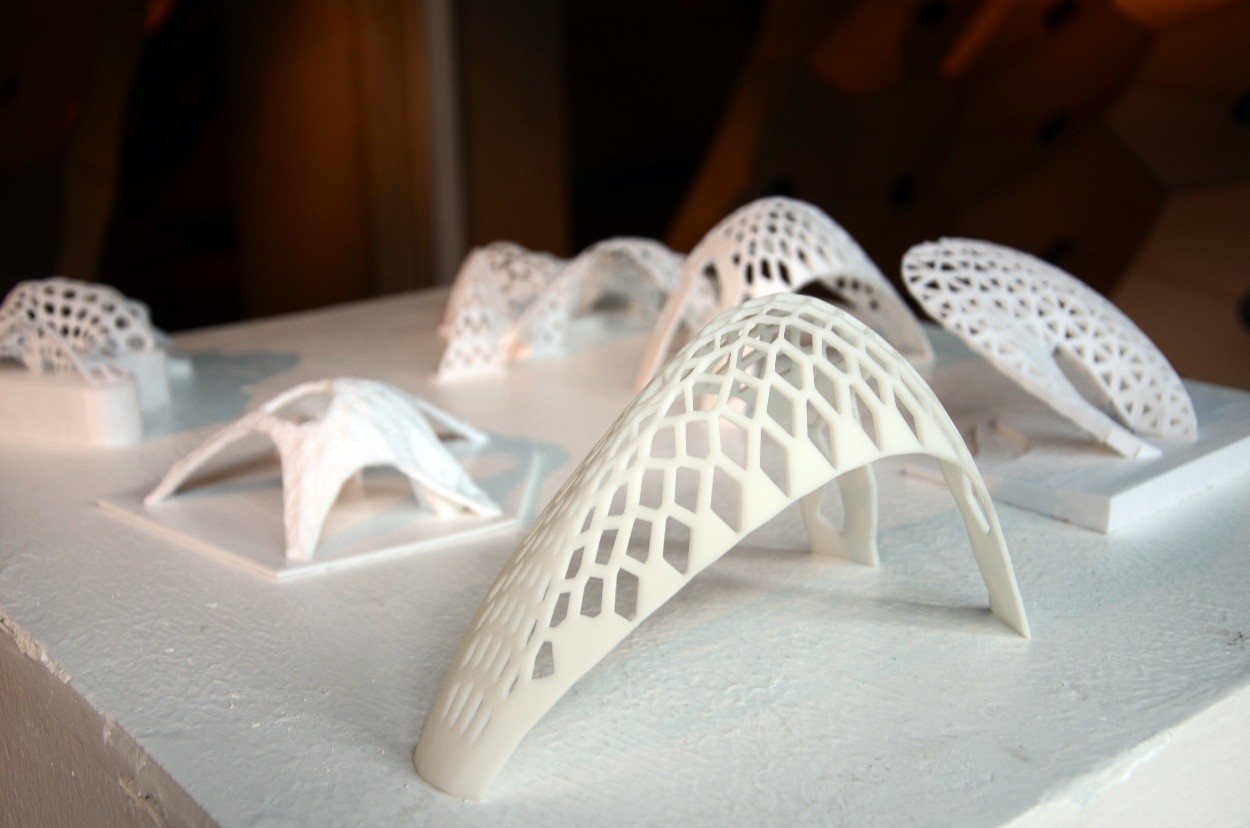
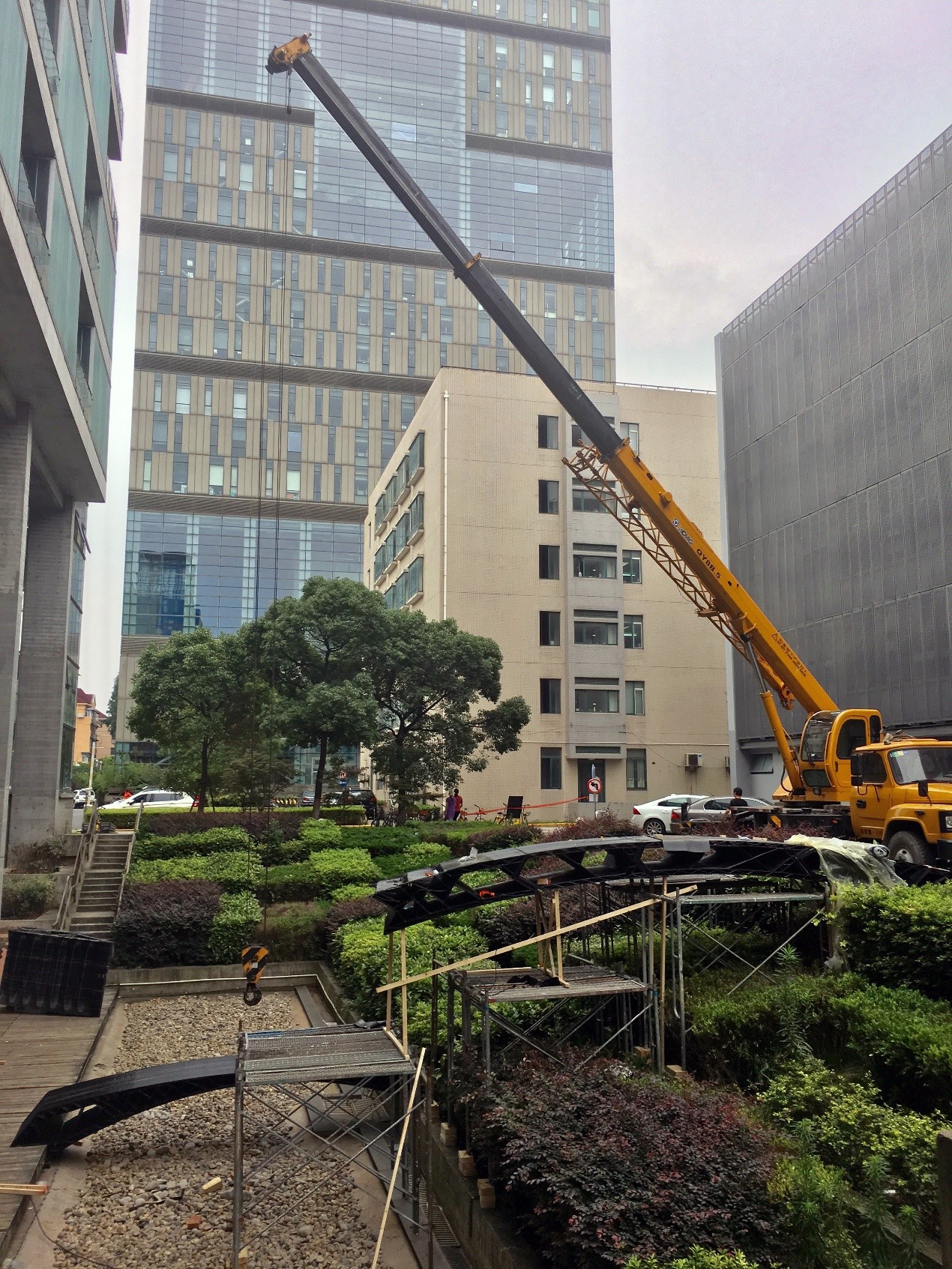
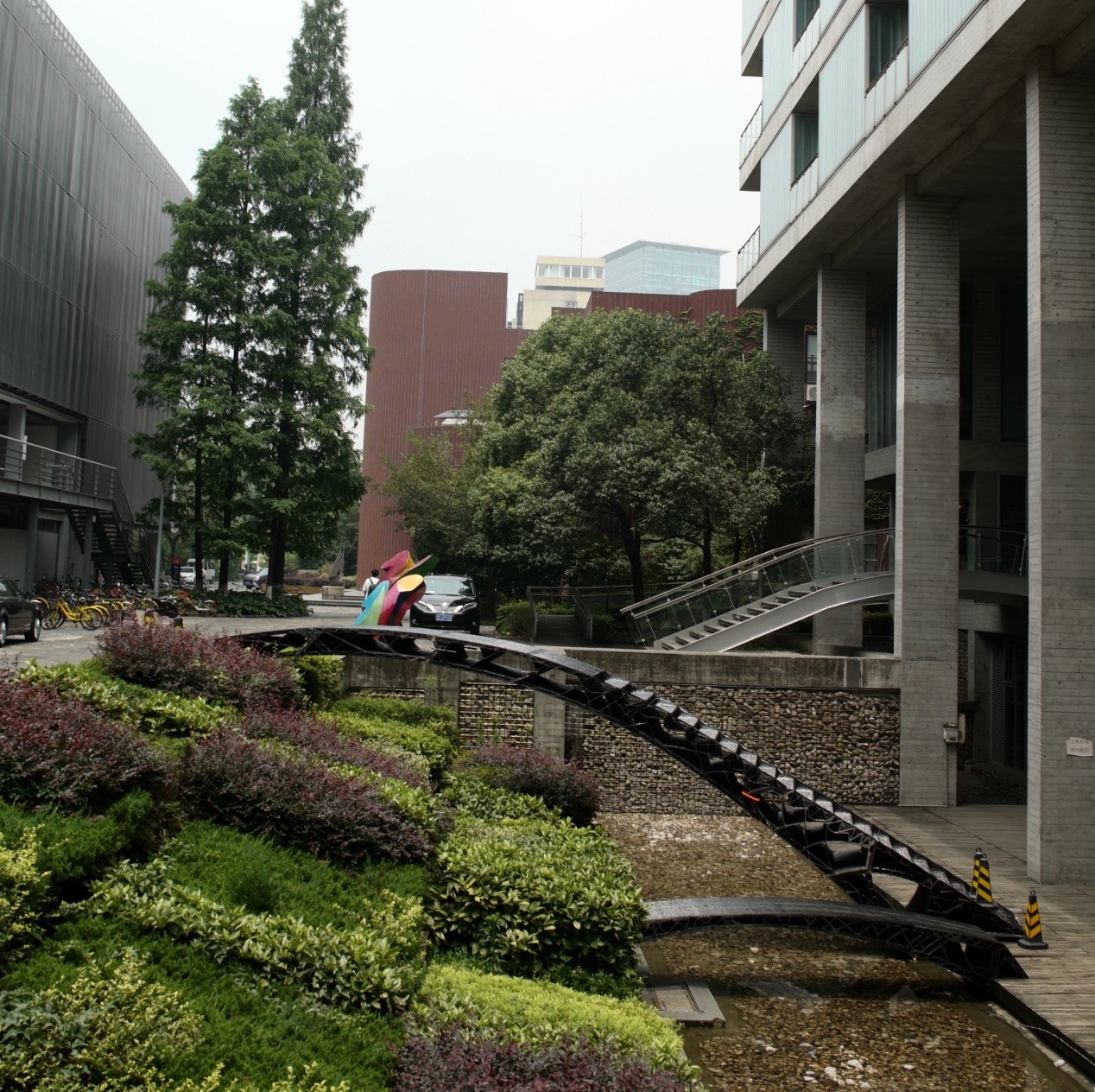
机器人平台为三维打印技术的发展与实现提供了新的可能性,无论是尺度上还是复杂系统打印上,机器人使得将三维打印技术应用于建筑领域的可行性被大大拓展。工作营基于传统三维打印的原理,结合结构性能化设计来探索建筑尺度三维打印的可能性与可行性。利用机器人三维打印实现定制单元的批量化生产,通过定制三维打印模块砌筑的方式完成两件三维打印桥梁,跨度分别为4米和11米,验证三维打印建筑产品的结构稳定性与可靠性。
Robotic platform provide new possibilities to the development of 3D printing technology. No matter in the printing size of the print of complex system, robot makes the feasibility of application of 3D printing technology in architectural field greatly increased. In this workshop, we base on the 3D printing technology and structural performance based design to explore the large scale 3D printing in architectural products.We use robotic 3D printing to achieve the mass production of customized components. Finally we print 2 bridges, 4m and 11m in span respectively, in which way the structural stability and reliability can be proved.





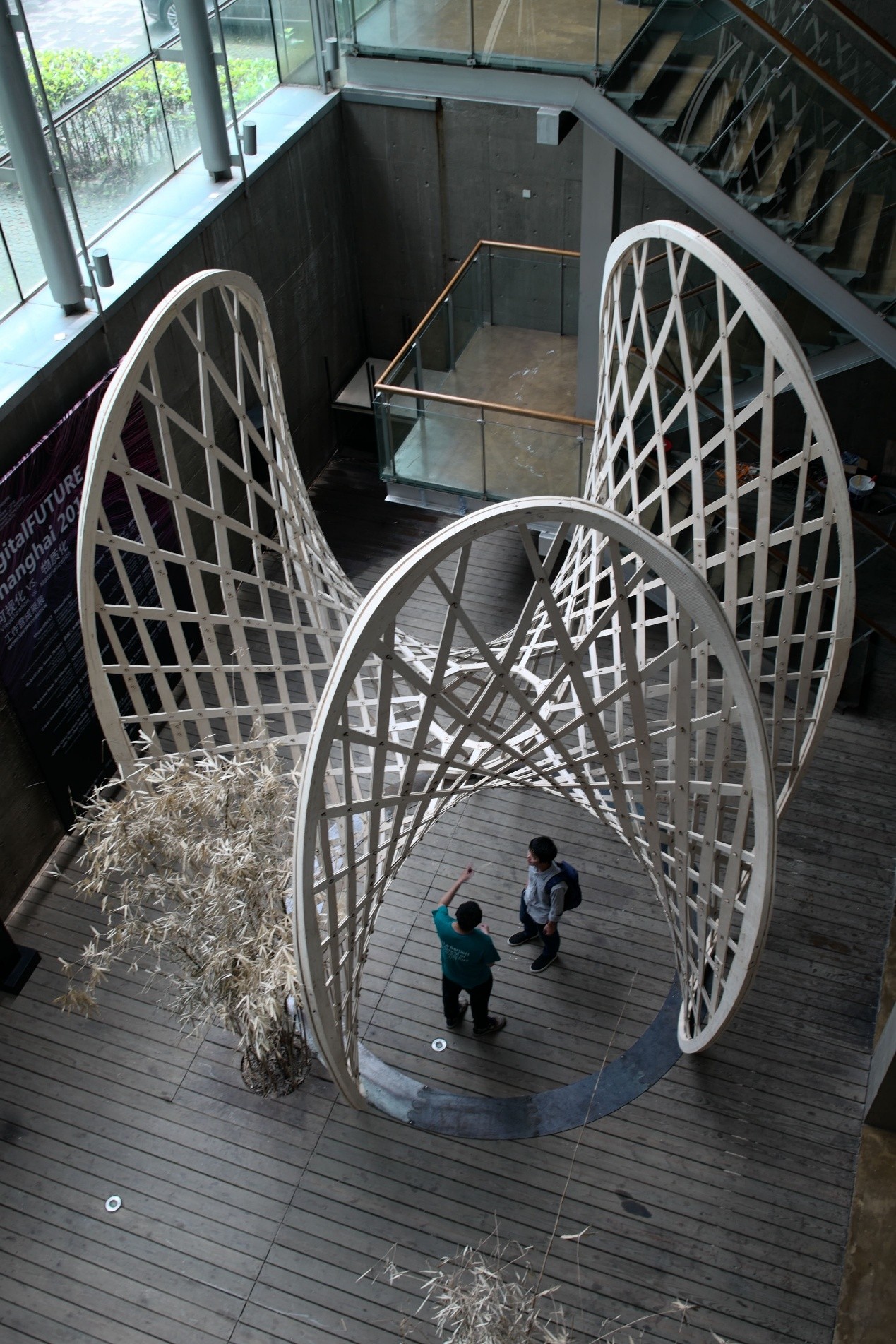
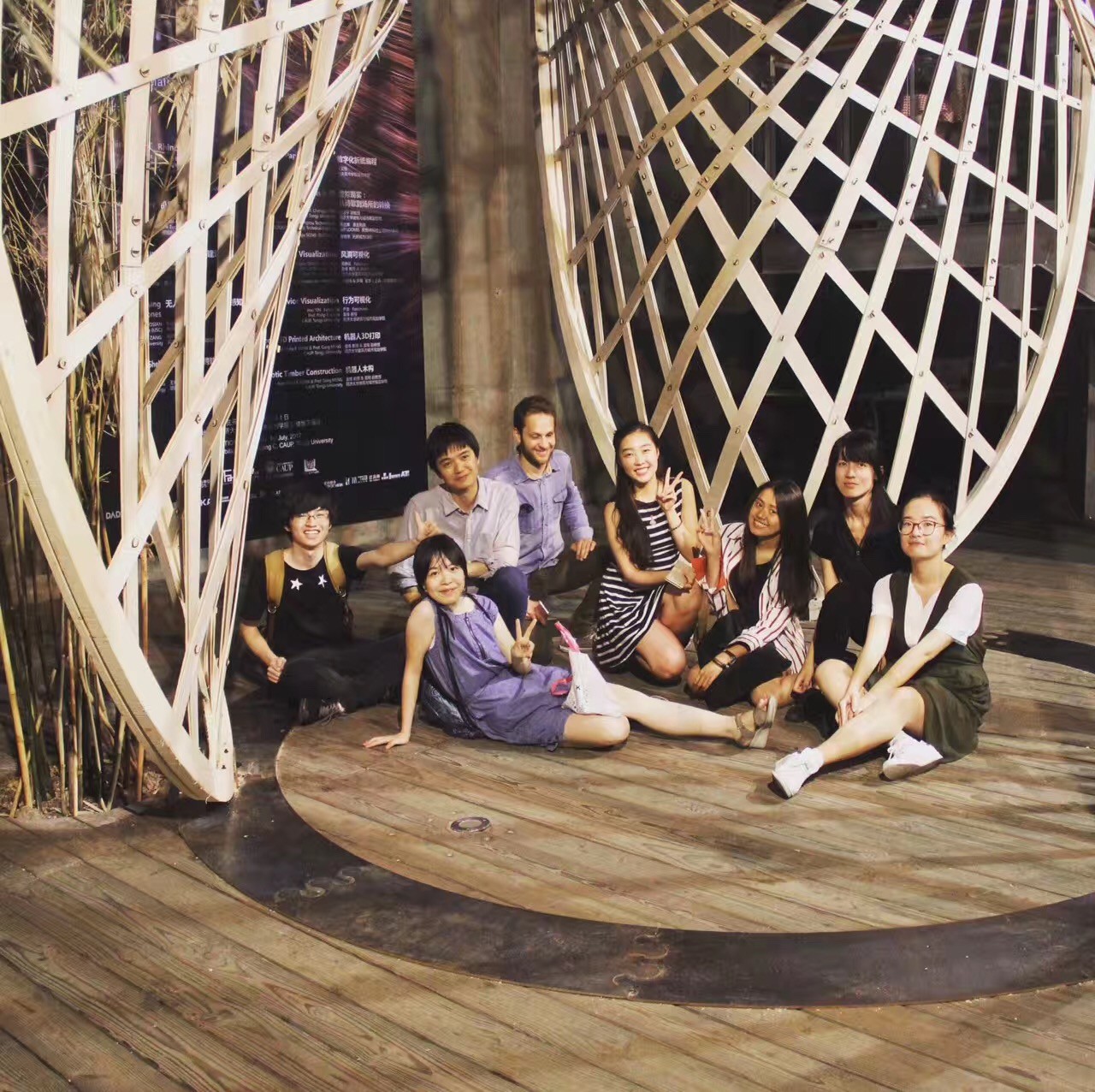
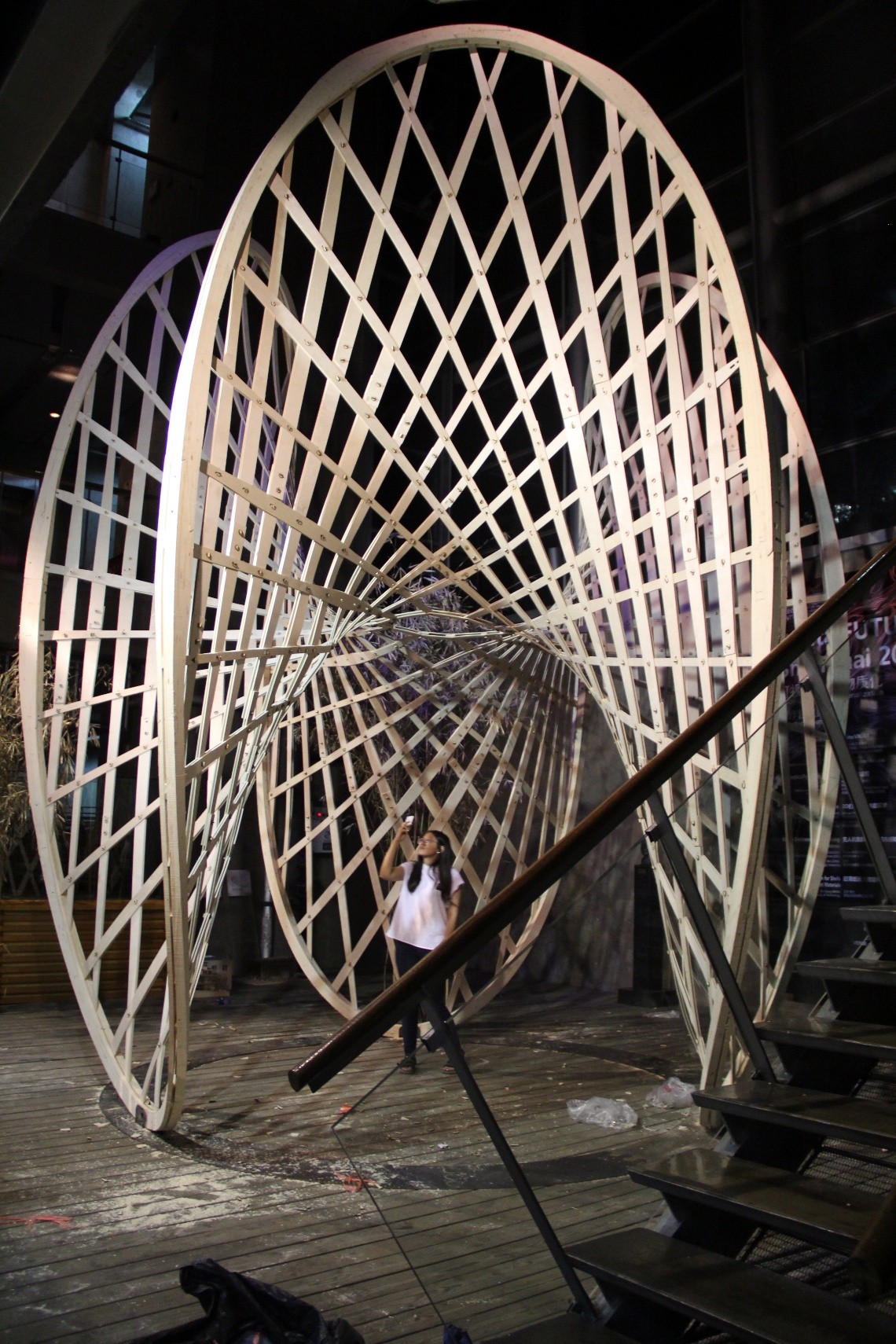
12. 机器人木构
指导团队:袁烽教授&孟刚副教授(同济大学建筑与城市规划学院)
柴华(FabUnion)
学生团队:Dario Marino,张瀛心,江旭莹,周博,吴宛霖,金晋磎,刘琳琳
工作营探索“结构几何”的设计方法在木构建筑设计中的应用,并以建筑机器人为工具,探索木构建筑的机器人数字建造工艺。工作营以木网壳结构为原型,探索“后期成形”的木网壳结构在自由曲面形式中的应用潜力。研究首先在设计平台上对自由曲面网壳结构的找形进行模拟与优化,然后通过结构性能模拟对网壳结构的构件尺寸进行优化,并利用机器人建造工具实现结构构件的批量定制生产。整个过程将材料特性、结构性能、形式设计与建造约束等因素的有机融合在空间木网壳结构的设计与建造过程中。学生将完成一系列木网壳结构原型的找形和结构优化研究,最终通过机器人建造工艺完成1:1的木网壳结构建筑原型建造。
The workshop aims to explore the "structural geometry" design methods and robotic fabrication approaches of wooden architecture. Taking the gridshell structure as the prototype, the workshop explores the potential of "post-forming" wooden gridshell in free-form structures. Firstly, the form-finding process of the free-form gridshells is simulated and optimized on the designplatform. Then, the dimensions of the gridshell members are optimized through structural performance analysis. Finally, robotic fabrication tools are used to make custom production of structural members. The whole process integrates the material properties, structural performance, form-finding method and fabrication constraints into the design and construction of the spatial gridshell structure. Participants will complete the form-finding, structural optimization and model-making of a series of gridshell prototype. And the final outcome will be a fullscale gridshell pavilion fabricated by robot.



供稿人:袁烽
主办单位HOSTS:

协办单位CO-ORGANIZERS:

赞助SPONSORS:


支持媒体SUPPORT MEDIA: